Ancient Egypt

Ancient Egypt
TODO: * Herodotus descriptions, including ** crocodile hunting (catch them by putting mud in their eyes!) ** tamed crocodiles in temples in Fayum
See also:
Article Objective
- this comprehensive outline covers ancient Egypt from prehistory to the fall of the New Kingdom
- article to be build up to cover subsequent foreign invasions up until Roman period (or another article to cover that)
- this article also reviews ancient Egyptian geography, technology, culture and religion.
A note about the "dynastic" chronology as used in this outline:
- most high school texts cover Egyptian history through the basic Old, Middle & New kingdoms chronologies
- the "dynasty" chronology used here (along with Kingdoms) is more complex but more comprehensive and accurate and accords to academic study of ancient Egypt
- teaching dynasties yields a more sophisticated student comprehension of ancient Egypt and the flow of time
- using dynasties makes more sense and does not add to the complexity of teaching the subject: rather, it simplifies and makes the subject more understandable
A note on format and tense
- this article may have inconsistent formatting
- this article may have inconsistent or variable use of tense
Notes & Objectives[edit | edit source]
The Study of Egypt offers meaningful opportunity to practice of:
apply historical concepts[edit | edit source]
- geography
- movement & isolation
- cultural diffusion & spread of ideas, technologies, and
- causality & human choice
- identity, especially in religion and culture
- stability v. change
- surplus & scarcity
- order v. chaos
- continuity v. change
cultural appreciation[edit | edit source]
- unique culture
- cultural influences
- gender roles
- cultural and technological advance
- art & architecture
other student enhancement[edit | edit source]
- engaging topic that students enjoy
- creative application in study
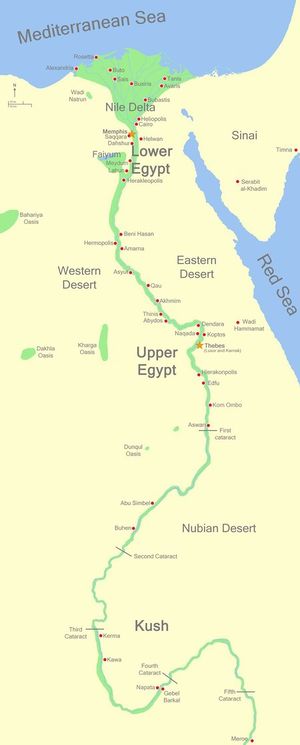
Geography[edit | edit source]
Nile River[edit | edit source]
Nile summary[edit | edit source]
- Nile Valley = ancient Egypt
- Egypt was accurately described by the ancient Greek historian Herodotus as "The Gift of the Nile"
- big idea here = "no Nile, no Egypt"
- Egypt = final 800 miles of the Nile as it runs northward to Mediterranean Sea
- longest river in the world: 4150 miles long!
Nile geographic characteristics and details[edit | edit source]
- flows north
- flows into Mediterranean Sea
- Nile Delta formed as flood waters spread out over coastal lowlands at river mouth
- the Egyptian words for "East" and "West" are the equivalent of "Right" and "Left"
- only "left" and "right" when facing upstream (i.e., facing south)
- so when facing upstream (south), East was to the right and West was to the left
- this affirms the importance to the Ancient Egyptians of the Nile and its unknown origins
- Ancient Egyptians thought the Nile began somewhere south of the Cataracts (falls)
- from underground sources
- sources = Blue & White Nile:
- White Nile from tropical, Central Africa
- Blue Nile from mountains of Ethiopia
- most water & silt = from Blue Nile
- June monsoon rains in Ethiopia = floods that bring silt downstream
- see Google Earth coordinates for Blue Nile source region >> todo
Nile Flooding[edit | edit source]
- length of river = long, slow flooding season in Egypt
- the Nile floods slowly:
- 3 months to rise & fall
- Egypt flood season = August to October
- slowly rises in August
- stays high September
- slowly recedes in October
characteristics of the Nile flooding[edit | edit source]
- Nile floods = predictable
- Nile floods = calm
- floods bring silt
- flood plains = farmland, but have to be re-organized every year
- Nile process formed Egyptian seasons of three, 4 month cycles:
- Akhet = flooding
- during flooding season, farmers were displaced and could serve as laborers for large projects such as pyramids and temples
- also during flooding season, shipment of stone and other goods by boat more extensive due to wider river flow
- for example, location of the pyramids = just beyond the flood plain
- during high flood period, Nile depth = 25-33 ft deep and current was more rapid = quicker movement
- Peret = growing season
- Shemu = harvest season (no rain)
- Akhet = flooding
appearance of the star Sirius marks flooding season[edit | edit source]
- the star, Sirius, announces the arrival off the floods
- also known as the "dog star"
- brightest start in the night sky
- when Sirius appears on the horizon after disappearing during the winter (blocked from earth's view by the sun)
- it marks the flooding season
- note the Greeks called the summer months the "dog days" when Sirius appears
periods of drought[edit | edit source]
- larger climate patterns led to times of weakened river flow and less flooding
- = periods of famine & political upheaval
- most important example = end of Old Kingdom and into the Middle Kingdom
Fayoum Oasis & Lake Moeris[edit | edit source]
- a basin in the desert to the west of the Nile in the upper part of Upper Egypt
- Nile floods fed the lake over time
- fed by the Nile and eventually connected to the Nile by Middle Kingdom pharaohs who improved irrigation in response to low flooding
- Middle Kingdom c. 2300 BC the lake was widened and the canal connecting it to the Nile deepened
- the lake served as reservoir for dry periods
- Egypt's most important oasis
- principal Neolithic site (early agriculture)
- has archeological evidence of earliest farming in Egypt
- site of the city Crocodilopolis (Greek name) or "Faiyum" (Arabic name)
- oases and water sources plenty by digging wells in lowlands alongside the Nile
- see by The History of the Fayoum Oasis by Jimmy Dunn, TourEgypt.net
Aswan Dam[edit | edit source]
- completed in 1970, built to control flooding
- located at "first cataract" >> = the northernmost waterfall
sources[edit | edit source]
- Nile River wikipedia article
- The Nile River by Marie Parsons, Touregypt.net
- The Waters of the Nile, PennState Online - article about archaeological work at Hierakonpolis with information about the water table at the dig site
Isolation[edit | edit source]
- Egypt isolated = development of unique culture
- still has some exchange and cultural diffusion with surrounding areas
- Egypt traditional boundaries are:
- from the series of waterfalls (cataracts) that define the southern-most navigation of the Nile
- to the Nile Delta where the river spreads out into the shape of a delta as it flows into the Mediterranean Sea
Movement[edit | edit source]
- the Nile flows North; dominant winds flow South
- this makes for easy navigation along the Nile:
- to go North: flow with the current
- to go South blow with the winds
- even after crossing the first cataracts, movement was even more difficult at the East-West direction bends of the Nile south of Egypt
- Note: many students become confused about which way a river flows -- all rivers flow downhill. With the Nile, downhill happens to be northward from the Nile's origins in the mountains of Ethiopia and the highlands of central Africa. See which way do rivers flow?
- flood season, with faster current = two weeks to move by boat northward from Thebes to Memphis
- low season, with slower current = two months to move the same
- this makes for easy navigation along the Nile:
- sources:
Regions[edit | edit source]
Ancient Egypt was divided into two principal geographic regions:
- Lower Egypt
- = northern portion, consisting mostly of the Nile Delta
- "downstream" thus "lower"
- Upper Egypt
- = southern portion, from the cataracts (waterfalls) to the Nile Delta
- "upstream" thus "upper"
- see below for details on geography and history of Lower and Upper Egypt
Natural Resources[edit | edit source]
summary
- ancient Egypt had bountiful resources, principally
- Nile river:
- provided water and silt for agriculture
- natural plants, especially papyrus (used for paper, baskets, boats) and flax (used for textiles and ropes)
- desert, salt beds, and nearby mountains providing:
- salts, copper, gold (especially from Nubia to the south), limestone, sandstone
- Nile river:
click EXPAND for details:
- Nile River provided for fishing, irrigation, movement
- silt carried by Nile replenishes the soil annually
- Nile Delta = extremely productive, fertile land that required irrigation for large scale farming
- Nile = one of the greatest agricultural regions of the ancient world
- core crops of ancient Egypt included:
- papyrus: for building, boats, and paper
- flax: for linen cloth and vegetable oil
- grains, such as wheat and barley
- fruits, such as figs, and melons and assorted vegetables
- herbs for cooking and medicine
- many animals living along Nile
- mining:
- sandstone
- limestone: abundant from mountains along Nile; soft stone can be cut with bronze tools
- good article on Limestone that can be used with students: Building Materials of the Pyramids Builders (touregypt.net)
- for literary connection see the poem, "In Praise of Limestone" by W. H. Auden, 1948 (wiki))
- complicated but interesting reference, as Auden discussed limestone as "that rock creates the only human landscape"
- abundant minerals in mountains, especially to southeast of Egypt, including copper, gold, lead
- Sinai provided copper, lead, turquoise
- Wadi Natrun
- a natural depression west of the Nile Delta with desert, minerals, and salty lakes and marshes that was an important source for:
- natron (for embalming)
- gypsum (for plaster)
- a natural depression west of the Nile Delta with desert, minerals, and salty lakes and marshes that was an important source for:
- Wadi Hammamat, desert region east of Thebes (Upper Egypt)
- principal mining region, supplying:
- basalts, quartz, gold, and sandstone
- principal mining region, supplying:
- resources that Egypt lacked and/or imported:
- lacked wood, and imported it from Lebanon and Asia Minor via the Phoenicians
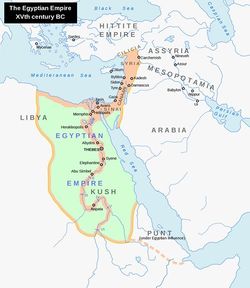
- imported minerals, metals, gems, dyes, and other goods from across the Mediterranean Sea region, the Middle East, Indus (India), and Nubia, Punt, and the Red Sea.
- sources
- Natural Resources in Ancient Egypt
- Geography of Egypt (wikipedia)
- farming in ancient Egypt - useful for students
Etymology/ Word Origins[edit | edit source]
- The word "Egypt" is a Greek reference to the river from the Egyptian word for "home of Ptah"; "Egypt" is commonly thought to mean "river" or "river valley," but it does not specifically mean that
- the anciet Egyptians called Egypt, "kemet," meaning "black land" for the fertile soil along the river
- the ancient Egyptians called the desert lands around the Nile, "deshret," meaning "the red land"
- "Nile" in Egyptian was "iteru" for "Great River"
Climate History[edit | edit source]
Sahara Desert & Climate Change[edit | edit source]
- during Ice Age desert was larger than today
- Note: according to Wikipedia, Antarctica is a desert, making the Sahara the second largest desert
- end of Ice Age brought rainfall, 8000BC - 6000BC
- prehistoric Egypt had more productive land around the Nile valley than later on, with extensive grasslands for grazing and hunting
- desertification commenced approx. 5500 BC and was complete by 3400 BC
Other periods of Climate Change in Egyptian history:[edit | edit source]
- 2200 BC sudden cooling and drying across Mideast, North Africa, Arabia, India, and other areas (including the Americas, which showed glacial advance in Canada and the Andes)
- 2150 BC sudden low floods of Nile contributes to collapse of Old Kingdom Egypt (the Akkadian Empire collapse in Mesopotamia and the Indus Valley decline are related events)
- 1800-1500 BC multiple volcanic eruptions, including mega volcano explosions at Mt. Vesuvius (1660 BC, Italy), Mt. Aniakchak (Alaska, 1645 BC) and volcano at Thera, Greek island of Santorini in 1650 (1620?) BC, cause climate disruption and cooling/drying ("volcanic winter" in Asia Minor, 1650 BC)
- Hyksos invasion likely a result of migrations across Mediterranean region and Middle East caused by climate disruption
- "Bronze Age Collapse" marked by decline, migration, and invasion across Mediterranean / Middle East, and coincides with collapse of Egyptian New Kingdom (see below and see also Sea Peoples)
- 1206-1186 BC: droughts in Eastern Mediterranean region
- 1000 BC Hekla mega volcano explosion in Iceland
- click EXPAND for later climate events in Egyptian history:
- 967-970 AD
- reduced Nile flooding in 967 AD leads to famine, plague and unrest
- 600,000 dead at Fustat, the first Arab capital of Egypt (under the Umayyad dynasty)
- 1064–1072 AD: Seven years' famine in Egypt
- 1201-1202 AD:
- reduced Nile flood leads to severe famines with chaos and unrest similar to that recorded in collapse of Old Kingdom records
- 1783: famine across Egypt
- 1/6th of the population perished
- caused by eruption of Iceland volcano Mt. Laki
- 967-970 AD
- sources:
- "The Fall of the Old Kingdom" from BBC.com
- List of Famines (wikipedia)
- Icelandic Volcano Caused Historic Famine In Egypt, Study Shows (Science Daily)
- sources:
| Stone Age to early Civilization | |
|---|---|
| Event | Date |
| Paleolithic Hunter-Gatherers with
semi-nomadic dwellings along Nile |
30,000- 10,000 BC |
| Neolithic period commences along Nile | 9,000 - 5,500 BC |
| boats with sails depicted on rocks | 6,000 BC |
| Egyptian calendar established with the
first recorded date being |
4241 BC |
| trade with Middle East;
linen weaving, household goods; |
4,000's BC |
| Sahara desertification causes
migration to Nile river valley by |
3,900 BC |
| extensive use of copper | 3,600 BC |
| donkey domesticated by | 3,400 BC |
| separate Upper and Lower Egypt
kingdoms solidify |
3300 BC |
| unification of Egypt under Menes
or "Narmer" |
3100 BC |
| Hieroglyphic Writing developed | 3100 BC |
Prehistory[edit | edit source]
Paleolithic Life in Egypt[edit | edit source]
- hunting, gathering, and fishing
- Nile Valley provides abundant food sources that support semi-nomadic lifestyle
- paleolithic buildings have been found at Wadi Halfa for semi-permanent habitation along Nile
- various paleolithic "cultures" starting during late Ice Age lived along the Nile and practiced fishing, grain grinding, tool making, pottery, and semi-nomadic lifestyles
- For more see: Here for wikipedia entry on Prehistoric Egypt
Neolithic Life in Egypt[edit | edit source]
- Neolithic Revolution & Settlement along the Nile come hand-in-hand
- organized farming starts approx. 9,000 BC
- fertile period of Sahara after Ice Age lends towards semi-nomadic, pastoral lifestyle
- settlements along Nile become permanent
- growth of villages and more complex societies
- growth of trade along Nile and with products from across Middle East
- planned farming and astronomy practiced by 6,000 - 5,000 BC
- see timeline for more
Upper and Lower Egypt overview[edit | edit source]
summary.
- traditionally Egypt is divided into two regions, as identified according to upstream (heading South) or downstream(heading North) along the Nile
- within these regions are "nomes," or autonomous local districts
- the nomes struggled for control and gradually unified to form Upper and Lower Egypt
- the origins of Egyptian culture, religion, and traditions came together during this formative period
- during "intermediate" periods between the Old, Middle and New Kingdoms, nomarchs asserted themselves
- nomarchs were either hereditary or appointed by a pharaoh
- see nomes(wiki)
Upper Egypt[edit | edit source]
- = "upper" for upstream (southern portion of Egypt)
- = from cataracts to the Delta
- = from cataracts to the entrance to the Nile Delta
- called by Egyptians "Ta Shemau" for "the land of reeds"
- Upper Egypt is narrow with smaller flood plain than Lower Egypt
- Upper Egypt is more easily unified, and harder to conquer than Lower Egypt
- originally divided into 22 nomes (districts or regional kingdoms)
- traditional capitals = Hierakonpolis (Nekhen), Thinis, and Thebes
- Thebes = central city of Upper Egypt
- Upper Egypt crown = "Hedjet" (white crown)
Lower Egypt[edit | edit source]
- = "lower" for downstream (northern portion of Egypt)
- = Nile Delta region
- called by Egyptians "Ta-Mehu" for "land of papyrus"
- = with Nile spreading out across large Delta, easier to invade and conquer, harder to control than Upper Egypt
- topography mostly swampy grassland
- at the Delta, the Nile breaks into multiple rivers:
- Pliny the Elder (N.H. 5.11) identified seven branches (from east to west): the Pelusiac, the Tanitic, the Mendesian, the Phatnitic, the Sebennytic, the Bolbitine, and the Canopic (source: Lower Egypt Lower Egypt (wiki))
- Nile flooding spreads across the Delta
- extremely fertile land with huge farm production
- Lower Egypt originally consisted of 20 nomes
- traditional capital = Memphis
- located at the "funnel" point of the Delta
- Lower Egypt crown = "Deshret" (red crown)
unification of Upper and Lower Egypt[edit | edit source]
- pre-pharaonic or pre-dynastic Egypt = time of conquest as larger sections of the Nile became unified under strong leaders.
- extensive irrigation, begun around 4,000 BC now becomes centralized and complex
- trade also motivated unification, which required agreement and standardization
- the Pharaohs represented their rule of all Egypt by combining symbols for Upper (White Crown or "Hedjet") and Lower Egypt (Red Crown or "deshret") into the "Double Crown" or "Pschent"
- for more see also the "Narmer Palette" which depicts Narmer's (also Menes?) unification of Upper and Lower Egypt approx. 3100 BC. The palette is one of the earliest artifacts with hieroglyphic writing
- see Menes & Narmer below
- see also myth of Osiris, Isis and Set below
Other regions[edit | edit source]
- Nubia and the Kush = regions to the south of Egypt
- western desert = arid desert with isolated oases that forms eastern portion of Libyan Desert
- eastern desert = arid and mountainous area that separates Nile Valley from the Red Sea
- Fayoum = large oasis just West of the Nile that was fed by the Nile during floods and with canals
- Sinai peninsula = arid land that bridges Africa and Asia to the east of the Nile Delta
standardization in and of Egypt[edit | edit source]
- trade = common weights, measures, and rules, and brings more discourse along the Nile
- religion standardized with greater unification
- different gods combined to be a single god with Egyptian unity
- power of the priests asserted with claim to control the flooding of the Nile and standardization of gods, temples, etc.
- see article: Nekhen, Greek Hierakonpolis for good study of the pre-pharonic city of Nekhen
- sources:
Menes, Narmer & 1st Unification of Egypt[edit | edit source]
Menes & Narmer[edit | edit source]
- = mythological first king(s?) of unified Egypt
- identified by Egyptian priest during the Ptolemaic or Greek period of Egypt in 300s BC
- Menes was possibly just a reference to the ruler(s)
- the name is from Manetho (wikipedia), the ancient Greek historian of Egypt
- Narmer = a king referenced in archeological finds
- likely the same as Menes
- associated with the god Horace
- we will refer to "Menes" as the same as "Narmer" hereout:
click on EXPAND for more on Narmer & Menes as first rule of unified Egypt
- unified through conquest
- first capital = Memphis, near the junction of Upper and Lower Egypt
- unclear if Menes or one of his successors actually created Memphis
- Memphis = important to control movement along the Nile
- myth of Menes that he was attacked by his own dogs while hunting
- he escaped by riding the back of a crocodile across Lake Moeris (a water body of the Fayoum oasis where pharaohs liked to hunt)
- this myth may be seen as an allegory for conquest/ unification of Egypt (attacked by his own dogs = enemies from within Egypt; crocodile = his power and chosen by the gods)
- Menes was supposed to have been killed by a hippopotamus
- Sources:

Pharaoh & Dynastic Periods[edit | edit source]
- Pharaoh = "Great House
- pharaoh = the ruling office, not a person, so different people could inhabit the position, including women at times
- rule of pharaohs divided into 20 "dynasties" or ruling families (later foreign rulers also chronicled according to dynasties)
- different families and dynasties controlled the position of pharaoh over time
- during New Kingdom the "pharaoh" became the ruler him/herself
- transfer of power from one dynasty to another = regional power struggle, especially during times of disruption
- pharaohs claimed descent from the gods and divinity (living gods)
- sources:
- pharaonic periods are:
- Old Kingdom
- intermediate period (disruption, unclear rule between kingdoms)
- Middle Kingdom
- intermediate period (disruption, unclear rule between kingdoms)
- New Kingdom
- intermediate period (disruption, unclear rule between kingdoms)
Transition of power between Dynasties & Kingdoms[edit | edit source]
summary.
- Old, Middle and New Kingdoms represent a united Egypt
- thus the Kingdoms have more stability
- intermediate periods represent a divided Egypt
- thus the intermediate periods are more chaotic
click EXPAND for causes of dynastic change
- causes of Dynastic change
- weak leadership, pharaonic personality
- internal family power struggles
- corruption
- rise of local leadership to challenge central rule
- power grab by vizier << or priests? >> find examples
- degree of crises
- crises change dynasties
- not as severe or of a more manageable nature
- critical mass crises that end end the Kingdoms
- are severe and unmanageable
- types of crises
- climate and/or monsoon season changes leading to Nile flooding irregularity and/or drought
- volcanic-induced climate change (see Thera explosion)
- plague
- external threats / invasion
- crises change dynasties
- consequence of collapse of dynasties
- interruption of projects
- consequence of collapse of Kingdoms
- rise of nomarchs
- regional competition
| "Kingdoms" or "Dynastic" Period | |
|---|---|
| Event | Date |
| unification of Egypt under Menes/Narmer | 3100 BC |
| "Archaic" or "Early Dynastic Period" of
state formation under unified Egypt |
3100-2686 BC |
| Old Kingdom begins | 2686 BC |
| reign of Djoser; orders construction
of the 1st major pyramid, the Step Pyramid |
2630-2611 BC |
| reign of Sneferu;builds three
pyramids including Bent Pyramid |
2613-2589 BC |
| reign of Khufu; builds Great Pyramid at
Giza; sons build 2nd Great Pyramid & Sphinx |
2589 - 2566 BC |
| severe drought due to larger climate
changes across Middle East & beyond |
2200 - 2150 BC |
| collapse of Old Kingdom
Egypt splits into separate states |
2150-2134 BC |
| First Intermediate Period | 2134-2055 BC |
| Middle Kingdom begins with reunification
of Upper & Lower Egypt by Mentuhotep II |
2055 BC |
| collapse of Middle Kingdom
with death of Queen Sobekneferu (had no heirs) |
1773 BC |
| Hyksos invasion & rule of Lower Egypt
migration & gradual conquest |
1720-1570 BC |
| Second Intermediate Period
Egypt divided; Hyksos rule of Lower Egypt |
1674-1535 BCE |
| New Kingdom begins with reign of Amhose I
who expels Hyksos rulers (1532 BC) |
1549 BC |
| height of of Egyptian empire under
Thutmose III who crossed the Euphrates River |
1458 BC |
| Battle of Kadesh (Ramses II fights the Hittites
in Syria and the war ends in a treaty) |
1274 BC |
| New Kingdom collapse | 1069 BC |
Old Kingdom[edit | edit source]

- consist of the 3rd through 6th "dynasties"
- distinguished from Archaic period by large-scale, centrally-controlled building projects
- = height of pharaoh central control
- = pyramid building
- capital at Memphis
- complex bureaucracy organized with vizier at head of government under pharaoh
- Palermo stone
- named for Palermo, Italy, where it resides
- from an Old Kingdom stone, or "stele" (a stone with writing engraved on it)
- which lists Old Kingdom and pre-Old Kingdom dynasties and kings
- various "fragments" exist and are stored at different museums
- known collectively as the "Cairo Annals Stone"
- the Palermo Stone lists mythological origin kings of Egypt and early Old Kingdom kings and dynasties
- it serves as a unique contemporaneous (from that time) historical evidence of the pre-dynastic and Old Kingdom Egypt
- other historical sources include:
- Manetho's chronology: c. 300 BC Greek or Egyptian priest who recorded a list, or "Annals", of Egyptian kings
- Royal Tablet of Karnack: lists Old Kingdom to 18th Dynasty
- Royal Tablet of Sakara: lists 58 kings from "Meibis" to Ramses the Great
- Royal List of Abydos: from the Temple of Sethos
- shows Ramses II and Sethos I paying homage to their ancestors
- and lists 76 names of prior kings
- the list does not give dates but creates a reference of names
- other sources are from individual engravings, steles, temples, etc. that list kings, dynasties, events, and years between them
- << to move this to its own section
- from "Gods, Graves and Scholars", p. 123-124
- see [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Imhotep Imhotep (wikipedia) for strong, genius vizier under Djoser (3rd dynasty)
Pharaoh as supreme leader[edit | edit source]
- 3rd dynasty pharaohs (the first of Old Kingdom pharaohs) established supreme rule
- pyramid construction begins = placement of pharaoh at top of Egyptian society and equal treatment to gods
- nomarchs relegated to local governorship at command of the pharaoh
- pharaohs claimed descent from gods (see Kings Lists)
- pharaohs commanded total authority and all the resources of Egypt
- pharaohs were both administrative and religious heads of state
- pyramids building can be seen as the height of pharaonic power:
- put enormous labor and resources to work for the pharaoh's temple
- see The Kings (Pharaohs) of Ancient Egypt (TourEgypt.net)
List of Old Kingdom Pharaohs[edit | edit source]
- Fourth Dynasty
- Hetepheres: Queen of Egypt during the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt (c. 2600 BC).
Golden Age[edit | edit source]
- 4th dynasty = Golden Age of Old Kingdom
- period of peace and economic expansion
- Sneferu (pharaoh)
- built three pyramids (see below)
- his son(s?) built 2nd Great Pyramid and the Sphinx
Weakening[edit | edit source]
- 5th - 6th dynasties
- massive pyramid construction weakened pharaohs
- less ambitious constructions (much smaller pyramids)
- occasional famine & breakdown of central control >> civil wars
- central control breaks down with local governors ("nomarchs") asserting power
- 5th dynasty marked by increased trade, ship building for trade in Mediterranean and Red seas
- attempts at reform ended up strengthening power of local nomarchs
Decline & Collapse[edit | edit source]
- 6th dynasty
- accelerated weakening of central rule
- expansion southward into Nubia, with canal construction around cataracts
- Pepi II = longest reigning pharaoh (94 years, although possibly 62 years; dies in 2184 BC)
- appointed two viziers, one each for Upper and Lower Egypt
- = sign of weakness and disunity
- impact of long reign =
- stagnation of rule (?)
- seems unlikely given the stability of the pharaonic system as ingrained political structure
- succession crisis due to long rule: heirs dying, competition for succession
- stagnation of rule (?)
- unclear that an aging pharaoh alone would cause collaps
- more likely scenario =
- succession crisis caused rivalries +
- gradual weakening of central rule +
- climate change = collapse
- 6th dynasty
Climate Change[edit | edit source]
- drought as Nile floods reduced due to lack of monsoons in Ethiopia
- crop failure & severe famine
- see accounts of famine and social collapse at
- the tomb inscription of the Nomarch of Hiarakonpolis with accounts of his attempts to bring order here: [inscriptions on walls at Ankhtifi (wikipedia]
- descriptions of destruction, famine, and chaos, likely about this period, from the [Ipuwer Papyrus] (wikipedia)
- collapse of central rule
- rival nomarchs compete for rule *Thebes dominant)
- sources:
Fall of Egyptian Old Kingdom from BBC History
First Intermediate Period[edit | edit source]
- period of disorder between Old Kingdom collapse and Middle Kingdom Rise
- accounts of ancient historian Manetho describe "70 kings in 70 days" =
- exaggerated but indicative of the chaos of the period
- Seventh to Tenth dynasties during this period
- two rival power centers at Memphis (at entrance to Lower Egypt) & Thebes (Upper Egypt)
- Template:Climate Change resulted in less discourse and trade along Nile
Middle Kingdom[edit | edit source]
- period of reassertion of pharaonic central authority and reunification of Egypt
- land reclamation and extensive irrigation as result of Nile reduction experience
- surplus agricultural production followed by economic and trade revival
- core Egyptian isolation ends with Hyksos invasion and fall of Middle Kingdom
Pharaohs[edit | edit source]

- Mentuhotep II, ruled 2061-2010 BC (approx)
- we Upper Egypt king who conquered Lower Egypt and reunited Egypt
- started the 11th Dynasty
- extensive irrigation projects
- economic revival
- pharaohs don't have same power as Old Kingdom pharaohs: regional leaders still strong
- Amenemhet I, ruled 1991–1962 BC
- possibly was the vizier to the last 11th Dynasty king, Mentuhotep IV
- seized power and started the 12th dynasty, the most prominent of Middle Kingdom dynasties
- land reclamation and irrigation projects
- return to normal flooding patterns under 12th dynasty
- economic recovery under him and successor pharaohs
- see Instructions of Amenemhat papyrus with poem on advice from father to son on ruling
- see also The Instruction of Merikare
- Senusret III, ruled 1878-1839 BC
- probably the most powerful Middle Kingdom ruler
- fully consolidated central rule over regional nomarchs
- led military expeditions, including to Nubia and into the Levant
click EXPAND for more
- to support expansion into Nubia, he built a navigable canal around the first cataract and numerous forts
- he bragged of his conquest of Canaan and ordered his successors to maintain the new borders:
Year 16, third month of winter: the king made his southern boundary at Heh. I have made my boundary further south than my fathers. I have added to what was bequeathed me. .... As for any son of mine who shall maintain this border which my Majesty has made, he is my son born to my Majesty. The true son is he who champions his father, who guards the border of his begetter. But he [who] abandons it, who fails to fight for it, he is not my son, he was not born to me. Now my majesty has had an image made of my majesty, at this border which my majesty has made, in order that you maintain it, in order that you fight for it.
- carried on irrigation projects, including to start a canal to connect the Nile to the Fayum Depression (or Fayyum; see entry here)
- through wealth and trade from conquests, urbanization increased under Senusret III
- Amenemhet III, ruled 1860-1814 BC
- maintained but did not expand the empire
- sent expeditions for trade and mining to the eastern desert and to Punt (southwestern coast of the Red Sea)
- continued work on the "Mer-Wer" (Great Canal) canal
- about 10 miles long and 1 mile wide
- connected the Nile to the Fayum Depression and fed Lake Moeris
- the project was completed by his son Amenemhat IV

- Sobekneferu, ruled 1806-1802 BC
- first fully confirmed Egyptian female pharaoh
click EXPAND for more
- daughter of Amenemhet III and possibly sister of Amenemhat IV
- Amenemhat IV had no heir
- her older sister, Neferuptah, was likely heir to Amenemhat IV (as she had a pyramid), but she died young
- so Sobekneferu assumed power upon Amenemhat IV's death
- Sobekneferu died after ruling four years
- she had no heirs and her rule marked the end of the 12th dynasty
- 13th Dynasty followed Sobekneferu
- lasted 154 years (1803-154 BC)
- was likely result of challenge to Sobekneferu
- marked by weakening of central rule and separation of the Delta region
- 14th Dynasty was likely Canaanite rulers
- ruled the Delta concurrently with part of the 13th Dynasty
- the 13th & 14th Dynasties are generally considered the last of the Middle Kingdom
- but they may also be seen as beginning of the Second Intermediate Period
end of Middle Kingdom[edit | edit source]
- possible droughts and crop failures contributed to decline
- droughts related to Greek volcano at Thera (Santorini), which caused/accelerated (?) sudden climate change associated with decline of Minoan Crete and Eurasian migrations (including Indo-Aryan) and migrations in Middle East, including that of the Hebrews & Caananites
- 12th dynasty declined and had succession problems
- followed by unrelated rulers (13th & 14th dynasties; power exchanged, fought over)
- Hyksos invasion -- migration, settlement (conquest?) of Nile Delta leads to final collapse of 13th dynasty and the Middle Kingdom
- Thera explosion is documented in the "Tempest Stele" (tempest means "storm"; "stele" is an upright stone monument))
- erected by the first New Kingdom Pharaoh, Amhose I, in 1550
- describes storms, dark skies, and damage to temples
- Amhose I claimed that he repaired the damage
Hyksos invasion[edit | edit source]
Summary
- Hyksos period = 1678-1570 BC
- Hyksos conquered Lower Egypt (Nile Delta region)
- Hyksos rule considered Fifteenth and Sixteenth dynasties that ruled Lower Egypt only

- Hyksos capital was at Avaras, in Northeast section of the Delta
- background:
- Middle Kingdom rulers were previously concerned with invasions and built defensive walls along the eastern border of the Delta (see
- therefore, invasions or excursions were an ongoing concern prior to Hyksos conquest of Lower Egypt
- Hyksos invasion possibly result of:
- food supply pressures in Middle East promote migration
- Middle Kingdom central control weaker than Old Kingdom
- Egypt further weakened by climate change and increasing migration
- "Asiatic" migration was gradual and eventually led to military conquest -- not a sudden invasion
- Delta region conquered by Hyksos was less unified than Upper Egypt which Egyptians were better able to defend
- impact:
- invasion/migration period = Egypt no longer culturally and technologically isolated
- Hyksos episode changes Egypt culturally and leads to Egyptian New Kingdom expansion and empire
- Egyptians adopt Hyksos war technologies, especially bows & arrows and chariots
click EXPAND for details:
- Hyksos were called "Asiatics" by the Egyptians (became general term for migrants from Middle East, including Hebrews)
- "Hyksos" comes from the Egyptian, "heka khasewet," for "rulers of foreign lands"
- Hyksos ruled Lower Egypt over a mixed population of Egyptians and Middle Easterners ("proto-syrians")
- Hyksos expelled by Upper Egypt pharaohs after adoption of Hyksos war technologies
- competing theories: conquest or migration or both?
- Conquest theory:
- told by the ancient historian Manetho
- armed, barbaric invasion
- Conquest theory:

- Hyksos employed technologies Egypt didn't have: composite bows, horses and chariots, and metal body armor
- note here about Egypt:
- Egyptian isolation meant that Egypt was immune from Middle Eastern warfare and its technologies;
- easy movement along Nile river meant Egypt didn't need long-distance animal-drawn transport
- Migration theory:
- climate change = a direct contributor to the Hyksos story
- dramatic cooling & drying across Eurasia also impacts Indian Ocean monsoons
- mega volcano explosion at Thera (Santorini), Greece, in 1650 BC
- Nile floods reduction weakens Egypt and disrupts food supply and trade patterns
- climate change and social collapse across Mediterranean and Middle East leads to migration and warfare across region and movement of people to larger food supply in Egypt
- climate change = a direct contributor to the Hyksos story
- Hybrid theory:
- combination of migration and invasion
- migration led to more exchange with Middle East
- armies derived from growing migration turned into invasion
- Hyksos culture
- = first wave of "Asiatics" to migrate to Egypt = larger exchange between Egypt and Middle East
- Hyksos culture absorbed into stronger Egyptian culture: language, religion (take on Seth as primary god)
- Hyksos rule becomes Egyptian
- Hyksos absorbed into Egyptian culture, but Egypt now culturally connected to and influenced by Levant peoples (eastern coast of Mediterranean Sea)
- primary source references:
- see The Instruction of Merikare for primary source indiciation of "Asiatic" invasions and settlements in Lower Egypt
- Genesis 43.15-18 on Hebrew migration to Egypt
- sources:
- Who Were the Hyksos? by Troy Fox (TourEgypt.net)
- Hyksos (wikpedia)
- Hyksos, Kings of Egypt and the land of Edom website publication of 1961 book; this source takes a biblical perspective and may be ahistocial to that extent
- The Hyksos: comparison between Hyksos and Vandals - the comparison is more useful for information about the Hyksos; potentially useful for World History students
Second Intermediate Period[edit | edit source]
- 1674 - 1549 BC (sometimes 1535 BC)
- period between final collapse of Middle Kingdom 13th & 14th dynasties and rise of New Kingdom 18th Dynasty
- 15th, 16th, & 17th dynasties
- 15th Dynasty = Hyksos rule of Lower Egypt
- 16th & 17th dynasties = Upper Egypt rulers coinciding with Hyksos rule of Lower Egypt
- Kamose, last king of 17th dynasty invaded Lower Egypt but failed to fully defeat the Hyksos
- Second Intermediate Period ends with rise of Ahmose I, ruler of Thebes, and the 18th dynasty in 1549 BC (sometimes 1550)
- Hyksos fully expelled by Ahmose I in 1532 BC at the Hyksos Delta region capital, Avaris
- from the [Rhind Mathematical Papyrus (wiki)], Amhose I claims:
Then there was fighting Egypt to the south of this town [Avaris], and I carried off a man as a living captive. I went down into the water—for he was captured on the city side—and crossed the water carrying him. ... Then Avaris was despoiled, and I brought spoil from there.

New Kingdom[edit | edit source]

summary
- 1550 BC - 1069 BC (approx)
- period of strong pharaohs and Egyptian foreign conquest
- period of great wealth, artistic expression, trade, and monument building
- marks Egyptian integration into surrounding regions through war, trade, and migration
- traditional capital of New Kingdom was Thebes, representing Upper Egypt the origin of New Kingdom rule
- growth of Egyptian merchant class
- individual wealth = democratization of pharaonic privilege such as tombs, mummification, etc.
- individual connections through trade with foreign lands
New Kingdom pharaohs[edit | edit source]
- the below is not complete, focusing on important persons and events
Amhose I[edit | edit source]
- first New Kingdom pharaoh (18th dynasty)
- conquers Hyksos
- then crosses Sinai into Middle East as far as Canaan (in the Levant) where the Hyksos were likely from
- first pharaoh to use horse and chariot (Hyksos technologies)
- invades and restores Egyptian rule over Nubia (to the South of Egypt)
- his son Amenhotep I built temples below the third cataract
- his grandson bragged of personally killing a Nubian king
- Valley of the Kings started by Thutmose I (grandson of Amhose I)
Amenhotep I[edit | edit source]
- Amenhotep means " "Amun is Satisfied"
- oversaw expansion of Egypt
click EXPAND for inscription in which Amenhotep bragged:
"And I ordered to build twelve warships with rams, dedicated to Amun or Sobek, or Maat and Sekhmet, whose image was crowned best bronze noses. Carport and equipped outside rook over the waters, for many paddlers, having covered rowers deck not only from the side, but and top. and they were on board eighteen oars in two rows on the top and sat on two rowers, and the lower – one, a hundred and eight rowers were. And twelve rowers aft worked on three steering oars. And blocked Our Majesty ship inside three partitions (bulkheads) so as not to drown it by ramming the wicked, and the sailors had time to repair the hole. And Our Majesty arranged four towers for archers – two behind, and two on the nose and one above the other small – on the mast with narrow loopholes. they are covered with bronze in the fifth finger (3.2mm), as well as a canopy roof and its rowers. and they have (carried) on the nose three assault heavy crossbow arrows so they lit resin or oil with a salt of Seth (probably nitrate) tore a special blend and punched (?) lead ball with a lot of holes (?), and one of the same at the stern. and long ship seventy five cubits (41m), and the breadth sixteen, and in battle can go three-quarters of iteru per hour (about 6.5 knots)...
- From the tomb of Amenhotep I (KV39).
- Source: [Egyptian technology (wikipedia)]
Thutmose II[edit | edit source]
- ruled 1493-1479 BC
- son of Thutmose I and a minor wife
- to secure power married his more-fully royal half-sister, Hatshepsut
click EXPAND for details:
- significant events during his reign include campaigns in Nubia and the Levant (eastern coast of the Mediterranean)
- the Kush kingdom rebelled upon Thutmose II's ascension as pharaoh
- Kush rulers tested Egyptian hold during transitions of power
- Thutmose II did fight in Nubia
- he may have led an expedition to Syria
- Hatshepsut may have been acting as a co-ruler
- historians dispute the length of Thutmose II's rule as either 14, 13, 10, or 3 years
- the Kush kingdom rebelled upon Thutmose II's ascension as pharaoh
- it is possible that Thutmose II was the "[Pharaoh of the Exodus"] (from the Jewish bible)
- evidence for it:
- his reign ended abruptly, leaving a two-year old heir
- cysts on his mummified body indicate possible plague
- evidence for it:
- see [Thutmose II (wiki)]
Hatshepsut[edit | edit source]

- 1508–1458 BC; ruled from 1479-1458 BC
- ruled as regent for Amenhotep's two-year old son, Thutmose III
- declared herself pharaoh and exercised full powers of pharaoh
- one of two Egyptian female pharaohs (with Sobekneferu of the Middle Kingdom)
- major accomplishments include expansion of trade networks & extensive construction projects
click EXPAND for details
- rule:
- daughter of Thutmose I who had no male heirs (giving her strong dynastic legitimacy)
- married half-brother, Thutmose II
- inherited rule from Thutmose II who died while her stepson was too young to rule (later Thutmose III)
- Thutmose III's mother was another wife of Thutmose II, Isit
- Hatshepsut had only one child, a daughter, Neferure
- Hatshepsut started as sole regent for Thutmose III as he grew up
- that she ruled as regent indicates that she exercised power during Thutmose II's reign, or at least at the end of it
- as Thutmose III grew up, she ruled as co-regent with him
- she then declared herself pharaoh
- she claimed to have been the legitimate successor of her father, Thutmose I
- from her burial temple, inscribed was Thutmose I's command:
"This daughter of mine, Khnumetamun Hatshepsut—may she live!—I have appointed as my successor upon my throne... she shall direct the people in every sphere of the palace; it is she indeed who shall lead you. Obey her words, unite yourselves at her command."
- Hatshepsut then exercised full power as pharaoh herself until her death
- Vizier = Senenmut, possibly from rule of Thutmose I, certainly inherited from Thutmose II
- as female pharaoh:
- wore pharaoh formal attire including the false beard for official events
- she was depicted in her time both in female and pharaonic dress
- she named herself "Maatkare" ("truth is the soul of the sun god")
- the name reinforced her legitimacy as representative of the god Amun
- Amun's proclamation of her rule was inscribed on a monument:
Welcome my sweet daughter, my favorite, the King of Upper and Lower Egypt, Maatkare, Hatshepsut. Thou art the Pharaoh, taking possession of the Two Lands.

- accomplishments:
- Hatshepsut focused on economic expansion of Egyptian trade networks
- re-established trade routes cut off by Hyksos invasions
- most famous trip was to Land of the Punt, an expedition down the Red Sea
- brought back 31 live myrrh trees
- sponsored massive building projects, including temples, obelisks, and statues
- she ordered built the tallest surviving obelisk at Karnak (one of two placed at the temple entrance)
- Hatshepsut focused on economic expansion of Egyptian trade networks
- inscription from her tomb at Deir el-Bahari
Hear ye, all persons! Ye people as many as ye are! I have done things according to the design of my heart. … I have restored that which was in ruins, I have raised up that which was unfinished since the Asiatics were in the midst of the Northland, and the barbarians were in the midst of them, overthrowing that which was made, while they ruled in ignorance of Re. He did not do according to the divine command until my majesty. When I was firm upon the throne of Re, I was ennobled until the two periods of years...I came as Hor-watit flaming against my enemies.
- erasure of Hatshepsut's legacy
- her stepson, Thutmose III and his son defaced and destroyed his step-mother's legacy by destroying her monuments and temples, defacing inscriptions and otherwise removing reference to her in his own inscriptions
- however, erasure was incomplete and focused only on the most public displays
- motives are unclear. Theories include:
- erasure occurred near end of Thutmose's life, indicating that it was more engineered by his son (he could have done it years earlier but chose not to)
- Thutmose's son, Amenhotep II, was worried about the integrity of his royal lineage, and targeted Hatshepshut to defame her to enhance his own lineage
- Thutmose resented being co-regent with Hatshepsut for so long and wanted to downgrade her legacy accordingly
- Thutmose's entourage wanted to elevate their own importance over those who served Hatshepsut
- Thutmose resented that a woman was pharaoh (not the strongest argument, as subsequent to Thutmose women served as co-regent and pharaoh)
- sources:
- Hatshepsut (wikipedia)
- http://discovermagazine.com/2011/jun/02-egypts-lost-fleet-its-been-found Egypt's Lost Fleet—It's Been Found Discover Magazine (article requires account for full access)
- teaching resources:
- 4:52 min video: "The Female Pharaoh" from PBS.org "Women's History Month"
Thutmose III[edit | edit source]
- reign: 1479 BC to 1425 BC
- son of a secondary wife of Thutmoese II, stepson and co-regent of Hatshepsut
- considered the "Napoleon of Egypt"
click EXPAND for details
- Thutmose died when Thutmose III was young
- Hatshephut, the primary wife of Thutmose II ruled on his behalf as "regent
- a "regent" = a ruler who rules on behalf of a young or otherwise incapacitated monarch
- as a young man he trained and acted as general
- he took power when he turned 20 << confirm
- Hatshephut, the primary wife of Thutmose II ruled on his behalf as "regent
- Egyptian enemies took advantage of the power gap between Hatshepsut and Thutmose III
- Thutmose III took advantage of the opportunity
- motives: wanted to exercise power, prove himself leader
- Thutmose III took advantage of the opportunity
- military genius
- given control of Egyptian armies by Hatshepsut
- conquests:
- conquered 350 cities in 17 military campaigns
- built largest-ever ancient Egyptian army
- expanded Egyptian empire across Syria as far as the Euphrates River
- conquered southward as far as Sudan
- inscribed historically accurate accounts of his campaigns at Karnak Temples of Amun
- click EXPAND for excerpt on the Battle of Megiddo:
His majesty set forth in a chariot of fine gold, adorned with his accoutrements of combat, like Horus, the Mighty of Arm, a lord of action like Montu, the Theban, while his father Amun made strong his arms. The southern wing of his majesty's army was at a hill south of the Qina brook and the northern wing was to the northwest of Megiddo, while his majesty was in their center. Amun being the protection of his person in the melee and the strength of Set pervading his members. Thereupon his majesty prevailed over them at the head of his army. Then they [the enemy] saw his majesty prevailing over them, and they fled headlong to Megiddo with faces of fear. They abandoned their horses and their chariots of gold and silver so that someone might draw them up into this town by hoisting on their garments. Now, the people had shut this town against them but they let down garments to hoist them up into this town. Now, if only his majesty's army had not given up their hearts to capturing the possessions of the enemy, they would have captured Megiddo at this time, while the wretched enemy of Kadesh and the wretched enemy of this town were being dragged up hastily to get them into their town, for fear of his majesty entered their bodies and their arms were weak for his serpent-diadem had overpowered them. * source: [https://www.ancient.eu/article/1102/thutmose-iiis-battle-of-megiddo-inscription/ Thutmose III's Battle of Megiddo Inscription (ancient.eu)]
- Sources:
Amenhotep II[edit | edit source]
- son of Thutmose III
- maintained the empire his father built via military campaigns in Syria
Amenhotep III[edit | edit source]
- ruled 1386 to 1349 BC
- peaceful period, few wars, diplomacy between rival powers
- crowned while still a child, ruled by a regent until age 13
- known as "Amenhotep the Magnificent
click EXPAND for details
- son of Thutmose IV
- period of prosperity and peace
- his son, Amenhotep IV changed his name to Akhenaton
- legacy
- has more surviving statues than any other pharaoh
- many texts from him survive
- his many diplomatic letters to rival empires survive
- Amarna letters << citation
- has correspondence with Assyria, Mitanni, Babylon and Hatti rules
- famously rejected Babylonian king's request to marry one of his daughters
- "From time immemorial, no daughter of the king of Egypt is given to anyone"
Akhenaten (Amenhotep IV) & Nefertiti[edit | edit source]

- reign: 1353 – 1336 BC
- also spelled Akhenaton
- son of Amenhotep III
- great-grandson of Thutmose III
- his queen =Nefertiti
- attempted monotheistic religion based on one god, Aten, a sun god, represented by a "sun disk"
click EXPAND for details
- in 5th year of rule, changed his name from Amenhotep IV to "Akhenaten" or "he who worships Aten" or "Living Spirit of Aten"
- he defunded temples to Amun (or Amon), which was his principal target
- priests and ruling classes did not accept his changes
- in response, he constructed a new capital on the East bank of the Nile, dedicated to Aten
- religious structures and power relationships over temples and gods were stronger than the pharaoh
- he was left to rule by himself in his new capital
- the city housed up to 50,000 residents
- it was abandoned immediately after his death
- legacy
- Syria lost to Hittites during his reign
- later pharaohs and the Egyptian establishment erased Akhenaten's legacy and his capital was abandoned
- some scholars find a connection between Akhenaten's monotheism and Judaism, with Akhenaten a precedent to Hebrew monotheism
- the story of Akhenaten demonstrates both the extent and limits of power of the pharaohs
- sources:
- Amenhotep IV (wikipedia)
- Akhenaen BBC
- Grim Secrets of Pharaoh's City -- describes dismal conditions of workers who built Akhenaten's city -- good article for students!
- Belief Of Akhenaten
Nefertiti
- wife & queen to Akhenaten
- her name translates to "The Beautiful Woman has Come"
- likely served as co-regent with Akhenaten during his last year and possibly as pharaoh outright
click EXPAND for details

- family lineage disputed, most likely:
click EXPAND for more
- father = likely, Ay, advisor to Amenhotep III and Tutankhamun
- mother ? perhaps Tey, wife of Ay, but only reference to her is as "nurse" to Nefertiti
- a theory is that an earlier wife, "luy" and Tey was Nefertiti's stepmother
- sibling theories:
- that Akhenaten and Nefertiti were full siblings is based on depictions of them as the sibling gods, Shu and Tefnut
- that her name, "The Beautiful Woman has Come," suggests she was born of a foreign mother
- Amenhotep III had a Mittani (mideastern) wife, Tadukhipa
- so it is supposed that she was Nefertiti's mother and thus half-brother to Akhenaten
- title as Egyptian queen = "Great Royal Wife"
- theories of her rule as co-ruler and/or pharaoh:
- that Nefertiti influenced Akhenaten to worship Aten (the sun god)
- depictions of Akhenaten and Nefertiti show them in equal proportions
- depictions show Nefertiti leading ceremonies and receiving diplomats
- co-regent:
- she may have ruled as co-regent with Akhenaten the year before his death
- if so, it suggests that he knew he was dying, perhaps of a plague
- a brief successor king to Akhenaten was named Neferneferuaten
- some believe this was Nefertiti
- thus naming her "Neferneferuaten Nefertiti"
- the suffix "aten" = same as "Akhen-aten", for the god "Aten"
- some believe this was Nefertiti
- there is little evidence for the succession of Akhenaten
- much evidence of his rule was erased by his successors
- she may have ruled as co-regent with Akhenaten the year before his death
the Hittite letters
- letter from an Egyptian queen to Suppiluliuma I, the Hittite ruler at Hattusa, the Hittite capital
- the letter reads
My husband has died and I have no son. They say about you that you have many sons. You might give me one of your sons to become my husband. I would not wish to take one of my subjects as a husband... I am afraid.
- Suppiluliuma supposedly replied:
Nothing like this has happened to me in my entire life!
- possible authors of the letter are Nerfertiti, her daughter, Meritaten, or Ankhesenamun, wife of Tutankhamun
- see [Hittite Letters (wiki)]
- sources:
- [Nefertiti (ancient.eu)]
- https://www.arce.org/resource/akhenaten-nefertiti-aten-many-gods-one Akhenaten, Nefertiti & Aten: From Many Gods to One (arce.org)]]
- [Nefertiti (wiki)]
- [The Bust of Nefertiti (Berlin Museum - which owns the bust of Nefertiti)]
- [Desperately Seeking Queen Nefertiti (National Geographic)]
succession of Akhenaten
- there seem to be two pharaohs between Akhenaten and his son Tutankhamun
click EXPAND for more:
- the order is a guess and could be in reverse
- evidence is uncertain; if so:
- Smenkhkare
- possibly co-regent with Akhenaten (before Nefertiti's co-regency)
- it is only speculation that Smenkhkare served as actual pharaoh
- portions of "wine dockets" (containers) mention "Regnal Year 1" or years 2-3 from the "house of Smenkhkare"
- see [Smenkhkare (wiki)]
- Neferneferuaten
- thought to be Nefertiti
- this pharaoh is thought to have moved the royal capital back to Thebes, thus ending the cult of Aten
- possibly, these were regents to Tutankhamun and not outright pharaohs
- "cartouches," a hieroglyph representing royalty, depict Smenkhkare and Neferneferuaten
- but that is not evidence enough of their ascension to pharaoh
- "cartouches," a hieroglyph representing royalty, depict Smenkhkare and Neferneferuaten
Tutankhamun[edit | edit source]
- reign: 1333-1323 BC
- son of Akhenaten
- minor pharaoh who assumed rule at young age and died at age 18
- famous mostly for the fact that his tomb and mummy were found intact & the mystery over his cause of death
click EXPAND for details
- his name was changed from "Tutankhaten" for "Living Image of Aten" (Akhenaten's god) to "Tutankhamun," meaning "Living Image of Amun,"
- Amun being the principle New Kingdom god and separating him from his father's legacy of worshipping Aten
- mother was commonly thought to be Nefertiti = incorrect
- DNA identified a mummy called by archaeologists, "Younger Lady" as his mother
- DNA shows that Younger Lady is a full sister of Akhenaten
- speculation that his death was murder = incorrect
- likely cause was a fatal infection following a broken leg bone
- his reign marks decline of 18th Dynasty
- he ruled for 9 years, dying at age 18
- Tutankhamun is famous because of the 1922 discovery of his intact tomb by the Englishman, Howard Carter
- the tomb was untouched with fabulous artifacts and riches, including his mummy
- by the 20th century, most ancient tombs had been ransacked and emptied
- see youtube video of the opening of the tomb Howard Carter and Tutankhamun's Tomb
- Tutankhamun's tomb was hidden behind another, later, pharaoh's tomb, which had been previously opened
- in the 1970s artifacts from his tomb were put on display and caused a sensation
- see Steve Martin's 1979 satire of the King Tut mania, King Tut (youtube)
- teachable moment = the line, "he died for tourism" !
- see Steve Martin's 1979 satire of the King Tut mania, King Tut (youtube)
- Sources:
Ay and Horemheb[edit | edit source]
- transition from royal line of 18th dynasty
- to bureaucratic / military leaders who installed themselves as pharaohs
click EXPAND for details:
Ay
- Ay, who is possibly Nefertiti's father, probably exercised power during Tutankhamen's reign
- Ay succeeded him as full pharaoh
Horemheb
- Horemheb succeeded Ay as pharaoh and was the last 18th dynasty pharaoh
- political divisions had grown under Akhenaten and his successors
- Horemheb reorganized the kingdom, consolidating power
- commenced the "erasure" of Akhenaten
- demolished monuments and art of the "Armana period" (period of Akhenaten and his successors)
- Horemheb was son-in-law of Ay
- Ay had tried to install is own son as pharaoh
- but Horemheb, who was chief general under Tutankhamun and Ay, took power for himself
- Horemheb chose Ramses I to succeed him
Ramses I & Seti[edit | edit source]
- 19th dynasty marks
- reorganization of Egyptian rule & empire
- military expansion
click EXPAND for details on Ramses I and Seti:
Ramses I
- ruled 1292-1290 approx
- short rule marked transition from 18th the 19th dynasties
- Ramses was from a military not royal family
- his name meant "Established by the strength of Ra"
Seti
- ruled 1290–1279 BC approx
- Seti's name meant "Man of Set, beloved of Ptah"
- Seti led military campaigns in to the Middle East
- conquest of Kadesh (in modern Syria) is his greatest military achievement
- Kadesh had been lost during Akhenaten's rule
- the Hittites soon re-conquered Kadesh
- conquest of Kadesh (in modern Syria) is his greatest military achievement
Ramses the Great[edit | edit source]
- Ramses II
- reign: 1279–1213 BC
- ruled for 66 years
click EXPAND for details
- 3rd ruler of 19th Dynasty, and consolidated power after weakening and collapse of 18th dynasty
- moved his capital to "Pi-Ramessess" in the Nile Delta
- launched invasions of Middle East from new capital
- location of new capital reflects Egyptian focus on Middle East trade and expansion
- also continued Egyptian rule and invasions of Nubia to the south of the cataracts, but less focus there
- first great achievement: defeated "Sherden" sea pirates who raided Egyptian trade in Mediterranean Sea
- his father Seti I had attempted to restore Egyptian Middle East rule, but was unable to hold onto Syria
- Ramses reconquered Syria
- The Battle of Kadesh (1274 BC):
- perhaps largest ever chariot battle with 5-6,000 total chariots
- Hittites (Asia Minor kingdom) opposed Egyptian expansion
- Employed mercenary forces, possibly Sherden forces (which would ultimately lead to weakening of Egyptian empire)
- Ramses ambushed but fought off near defeat
- battle indecisive
- resulted in first diplomatic peace treaty
- Ramses returned to Egypt and declared victory
- inscriptions at Luxor brag:
"His majesty slaughtered the armed forces of the Hittites in their entirety, their great rulers and all their brothers ... their infantry and chariot troops fell prostrate, one on top of the other. His majesty killed them ... and they lay stretched out in front of their horses. But his majesty was alone, nobody accompanied him "
- source: Ramesses II (wikipedia)
- Ramses II is often portrayed in popular culture as the pharaoh of Old Testament's Book of Exodus (Moses)
- sources
- Battle of Kadesh (wikipedia)
- sources
Collapse of New Kingdom[edit | edit source]
- following the death of Ramses II, was a series of pharaohs who oversaw a decline in Egyptian power
- Ramses II outlived many of his own sons (died in 1213)
- his thirteenth son, Merneptah, was selected as heir after the death of older brothers
- Merneptah was about 70 years old when he became pharaoh
- over-expansion and constant warfare weakens Egyptian empire
- climate change impacts region: more migration into Egypt & destabilizing invasions
- a possible cause is the Hekla 3 volcanic eruption in Iceland
- Egypt suffered crop losses and inflation in grain prices
- famines resulted
- economic decline coincidental to decline of Hittite Empire
- Bronze Age collapse:
- Egypt suffered from reduced flow of the Nile and overall dryer and cooler climate
- however, Egypt remained intact while most eastern Mediterranean states collapsed
- Hittite empire fell, Mycenaean Greece collapsed, Assyria weakened, etc. see Bronze Age Collapse entry
- Sea Peoples:
- "mysterious" raiders
- likely from Italy, Greece, and the Levant who raided coastal areas of Eastern Mediterranean
- Ramses III, from the 20th Dynasty (Ramses II was in 19th Dynasty) ruled 1186-1155
- considered the last great pharaoh of the New Kingdom
- held off the Sea Peoples
- famine conditions during final years of his rule may have been caused by a volcanic eruption in Iceland (possibly 1159 BC)
- may have been murdered
- the "Harem conspiracy", a failed coup led by one of the wives of Ramses III who wanted her son to take over from Ramses III
- the conspiracy shows that there was political instability
- 38 people were tried and executed
- following Ramses III, Egypt lost control of its rule in the Levant
- Libyan and Nubian invaders threatened Egypt and took territory
- the last New Kingdom pharaoh was Ramses XI, who died in 1078
- by that time the High Priests of Amun controlled Thebes and Upper Egypt
- Smendes took over as pharaoh and founder of the 21st Dynasty, ruled 1077/76–1052
- Smendes ruled over a divided and weak Egypt that was invaded by other peoples, including the Libyans (from the west, controlled the Delta), Kushites (from the south, established themselves as pharaohs) and later on by the Babylonians, Assyrians, Persians, Greeks under Alexander the Great and, marking the end of pharaonic Egypt, the Romans
Post-Egyptian self-rule[edit | edit source]
- Berber rule
- Amazigh people
- see https://phoenicia.org/berber.html
- Nubian rule
- Assyrian rule
NOTE: to create new section for post-New Kingdom through Ptolomaic rule
Architecture[edit | edit source]
- Egyptian architecture was defined by the available resources and geography:
- sandstone
- Nile valley and Nile flooding
- Nile floods allowed for transport of massive rock cuttings
Obelisks[edit | edit source]
Pyramids[edit | edit source]
early tombs & monumental structures[edit | edit source]

- early Egyptians built elaborate underground burial tombs for kings & elites
- these underground tombs began to build up above ground with mud bricks
- mastaba
- = Arabic term for "bench of mud"
- ancient Egyptians called it, "house of stability"
- rectangular, flat-top, mudbrick structure, up to 30 ft high
- bricks were made of clay from the Nile banks, formed and sun-dried
- possibly related to similar Mesopotamian structures
- mastabas were built to protect burial grounds from animals and robbers
- mummification began with these structures, as they did not allow for natural mummification in the ground
- features included:
- chapel-like area above ground for ceremonies and offerings of food & other funerary offerings for the dead
- the chapel area had a false door to protect against robbers
- oriented North-South, which was important for the buried's access to the afterlife
- two underground chambers, one for the dead and another for materials & goods for the afterlife
- chapel-like area above ground for ceremonies and offerings of food & other funerary offerings for the dead
- mastabas were continued to be built into the Middle Kingdom
- increasingly complex over time
- some structures began to take shape of pyramids, which were adopted for kings
Benben stone[edit | edit source]

- in the Egyptian creation myth (see below) a pyramid-shaped land rises from otherwise empty waters, a "primeval mound" called "Benben"
- thus the Benben represents creation and the origin of the sun
- early Egyptians built large earth mounds to represent the the rising land of creation, which was subsequently represented in a pyramid shape of a single block of stone, thus the Benben
Old Kingdom early pyramid building[edit | edit source]
- Step Pyramids
- were the 1st pyramids
- built in layers much like Sumerian ziggurats
- considered "true pyramids"
- gaps between "cake layers" of step pyramids filled in to form smooth surface
- used limestone casings
- the capstone, or tip, of the pyramids (and obelisks), called the "pyramidion," were covered in gold leaf, likely to reflect the sunlight and thereby mimic the Egyptian origin myth of the "benben" (see below)
click EXPAND for details on step pyramids
- Djoser (3rd dynasty, ruled 2691 to 2625 BC):
- built the 1st pyramid at Saqqara, northwest of Memphis
- step pyramid, construction overseen by the famed vizier, Imhotep
- his 3rd dynasty successors, Sekhemkhet, Khaba and Huni never completed their own pyramids
- Sneferu (4th dynasty, 2613-2589 BC) credited with building three pyramids (all at Dahshur)

- Meidum pyramid
- started for Huni
- Sneferu took over construction and had the steps filled in to form true pyramid
- abandoned construction perhaps due to perceived instability and steep slope (51 degrees)
- it further collapsed during New Kingdom
- Bent pyramid
- very steep at base (55 degrees), then a gentler rise near top (43 degrees) make it look "bent"
- importance of this pyramid is that it is the last in the transition from step to "real" pyramids
- the pyramid has a unique passageway between the pyramid and a smaller one that was built for his queen, presumably so that he could visit her in the afterlife
- Red pyramid
- (3rd largest pyramid at 345 ft)
- = first "true pyramid" designed and built for smooth surface
- was tallest structure ever built before Giza
- not actually red, but with white limestone casing gone, the stone below is red
- angled at 43 degrees = less steep than Great Pyramids
- took 10 - 17 years to build
- Snefuru was probably buried here
- Meidum pyramid
Great Pyramids[edit | edit source]

summary
- at Giza built by the 4th dynasty pharaohs:
- the Great Pyramids at Giza include:
- Khufu (also "Cheops") = "The Great Pyramid"
- Khafre (also "Chepren")
- Menkure (also "Menkaure")
- The Great Pyramid of Giza (Khufu or Cheops pyramid)
- at 480.6 ft = tallest pyramid and was tallest building in the world until the 1300s AD
- the only remaining intact of the Seven Wonders of the World
- 20 years to construct
click EXPAND for details
- other statistics & notes:
- incline is 51 degrees
- 2.3 million limestone blocks were quarried nearby the construction site
- the 144,000 limestone used for the casing (surface) was from the Tura quarry, which yielded a white stone; Tura was about ten miles from Giza on the opposite side of the Nile.
- granite beams to build the inner chambers were shipped 580 miles from Aswan (first cataract) - a distance about from Washington DC to Chicago
- accuracy of the lines of the four sides pyramid is to within 57 mmm
- the ratio of the base perimeter to the height in ancient Egyptian measurement ("cubits") = 2π, wihch indicates that the Egyptians were aware of the value of π (contrary theory is that they were obsessed with creating a proportionally perfect triangle that just happens to = 2π)
- Cheops is the only pyramid to have burial chambers above ground (very complex to build)
- for more statistics see:
- other statistics & notes:
- Khafre pyramid at Giza
- second largest pyramid at 448 ft, and has a steeper angle of incline than Cheops at 53 degrees
- looted after collapse of the Old Kingdom
- Menkure pyramid at Giza
- at 204 ft, the smallest of the three Great Pyramids (about the height of the Step Pyramid of Djoser)
click EXPAND for details
- Labor
- the ancient Greeks claimed that the Egyptians built the Great Pyramids with slave labor
- archaeological records show that skilled, paid labor was used, primarly from the farming workforce, perhaps 100,000 workers for Cheops
- Pepi II's pyramid
- Pepi II was the last important Old Kingdom pharaoh, (reigned 2279-2184 BC)
- built the last pyramid of the Old Kingdom
- built at Saqqara, has large complex with three satellite pyramids (2 for wives)
- 172 ft high and a "true pyramid" = substantial construction, but modest in size compared to Great Pyramids
- indicative of Old Kingdom decline
Subsequent pyramid building
- First Intermediate Period constructions were smaller and not full pyramids, indicative of inability to command resources
- Amenemhat I, the first Middle Kingdom pharaoh reestablished substantial pyramid building, but not on the scale of Old Kingdom pharaohs
- later pyramids were constructed of mud & brick, with stones used for casing only (cheaper, easier build)
- the only New Kingdom pyramid was built by Amhose I, the first New Kingdom pharaoh
- was the last pyramid
- constructed of mud and brick with limestone casing
- built as a monument, not a tomb
- subsequent New Kingdom tombs were placed in mortuaries such as Deir el-Bahari and the Valley of the Kings
- Wealth burial and Looting
- with the treasure buried with the pharaohs in pyramids and tombs, the Egyptians stored away enormous wealth
- pyramids, temples, and tombs were robbed over time, but most frequently they were targeted during periods of disorder, scarcity and famine, especially during the First Intermediate Period during which the Nile flooding was reduced and famine and chaos ensued
- during these times, respect for the pharaoh and the afterlife becomes less important than necessity
Nubian pyramid building
- built by Kingdom of Kush rulers who conquered Egypt (25th Dynasty of Egypt)
- were built in the Nubian homeland along the Nile
- first pyramid built in 751 BC at El Kurru, a royal cemetery
- emulated ancient Egyptian pharaonic practices
Pyramid building & engineering[edit | edit source]
- materials
- Old Kingdom pyramids were built of stone
- early Old Kingdom pyramids were made entirely of limestone with gates, ceilings and walls of burial chambers and the outer casing made of high-quality limestone or granite
- the Great Pyramids are Old Kingdom constructions
- Middle Kingdom pyramids
- Middle Kingdom pyramids were built of piled mud-bricks covered with limestone
- later pyramids were built on hills to reduce the amount of brick and stone required
- Old Kingdom pyramids were built of stone
- construction
- Ancient Egyptians were expert rope builders

- they understood the utility of tension and leverage
- they understood that an incline, or a ramp, spreads the force required to lift a heavy object across the distance of the incline
- click EXPAND for excerpt from wikipedia entry on how an incline helps to life heavy objects:
An inclined plane, also known as a ramp, is a flat supporting surface tilted at an angle, with one end higher than the other, used as an aid for raising or lowering a load. The inclined plane is one of the six classical simple machines defined by Renaissance scientists. Inclined planes are widely used to move heavy loads over vertical obstacles; examples vary from a ramp used to load goods into a truck, to a person walking up a pedestrian ramp, to an automobile or railroad train climbing a grade. Moving an object up an inclined plane requires less force than lifting it straight up, at a cost of an increase in the distance moved. The mechanical advantage of an inclined plane, the factor by which the force is reduced, is equal to the ratio of the length of the sloped surface to the height it spans. Due to conservation of energy, the same amount of mechanical energy (work) is required to lift a given object by a given vertical distance, disregarding losses from friction, but the inclined plane allows the same work to be done with a smaller force exerted over a greater distance.
- Source: [Inclined Plane (wiki)]
- click EXPAND for sources and readings on pyramids
- [The World’s Oldest Papyrus and What It Can Tell Us About the Great Pyramids (Smithsonian Magazine)]
- [Pyramids at Giza (National Geographic)]
- Why the Ancient Egyptians Built Pyramids - A matter of Religion
- 4th Dynasty (wikipedia)
- List of pyramids (wikipedia)
- Building the Great Pyramid
- Nubian Pyramids (wikipedia)
Sphynx[edit | edit source]
- see Luxor dromos, aley of sphynxes
temples[edit | edit source]
Religion[edit | edit source]
- not counting pre-dynastic period, the distinct Egyptian civilization lasted over 2,000 years
- therefore, Egyptian religion, myths and gods change (morph) over time
- additionally, across the 800-mile stretch of the Nile, different regions held varied views of the gods & myths
- across ancient Egyptian history gods and stories are intermixed or merged, or derived from one another
Egyptian cosmos[edit | edit source]
- Egypt = center of earth
- Nile = center of Egypt, and life-giving, fed by Heavenly River at its source
- relate to Egyptian isolation and as source of trade (others come to Egypt)
- beliefs:
- earth flat, oval, with Nile running through the center
- mountains surround Egypt with "Heavenly River" on outer edge
- Egyptians unaware of Nile sources, believed it was the Heavenly River
Atum and the origin myth[edit | edit source]
- "Nun" is the empty, divine place of origin of the universe
- the Benben, a pyramid-shaped jut of land that arose from the waters (chaos) of Nun
- the creator god Atum lived on the Benben
- the Benben, therefore, would be the first land to be lit by the sun
- the god Nu is depicted as a human with a frog's head or as a baboon, and holds the sun disk while standing on the Benben
- the Benben is thought to have inspired the shape of the pyramids and the pointed top of obelisks
- Nun is depicted in Middle Kingdom and later temple walls as "the father of the gods"
- Ra displaces Atum in the New Kingdom
- Sources:
Ra[edit | edit source]
- Ra is the sun god and creator god
- identified with the "noon sun"
- Ra is either merged with or a later version of Atum
- Atum was subsequently referred to as Atum-Ra
- Old Kingdom pharaohs were considered "Sons of Ra"
- Middle Kingdom depictions or Ra merged with Atum (or Aumn)
- New Kingdom depictions of Ra focused on his role as carrier of souls of the dead on the "sun boat"
Amun[edit | edit source]
- was the principle deity of Thebes (Upper Egypt's principal city)
- in New Kingdom became the principal Egyptian deity, the creator, replacing Atum and Ra
- was called Amun-Ra
- New Kingdom Egyptians credited Amun with defeat of the Hyksos
- thus he became protector of the poor or upholder of justice or "Ma'at" (also truth and goodness)
click EXPAND for inscription from an artisan's village on Amun:
[Amun] who comes at the voice of the poor in distress, who gives breath to him who is wretched..You are Amun, the Lord of the silent, who comes at the voice of the poor; when I call to you in my distress You come and rescue me ... Though the servant was disposed to do evil, the Lord is disposed to forgive. The Lord of Thebes spends not a whole day in anger; His wrath passes in a moment; none remains. His breath comes back to us in mercy ... May your kꜣ be kind; may you forgive; It shall not happen again.
- Amun worship became a powerful cult and was merged with Ra into "Amun-Ra"
click EXPAND for text from "Hymn to Amun-Ra"
Lord of truth, father of the gods, maker of men, creator of all animals, Lord of things that are, creator of the staff of life.
- from [Amun: Early History (wiki)]
- the pharaoh Akhenaten attempted to suppress the cult of Amun
Atum's children[edit | edit source]
- having arisen from the waters, Atum created the air and the earth
- Atum coughed up or spat out:
- Shu, god of the air
- since the air cools, Shu was a god of pacification
- Tefnut, goddess of moisture and rain
- Shu, god of the air
- Shu and Tefnut had two children:
- Geb, god of the earth
- he created earthquakes and allowed crops to grow
- he was associated with healing as well as snakes
- Nut, goddess stars (thus of the nighttime) and the sky in general
- Nut was considered a goddess of protection (depicted as a cow or tree covering the sky)
- Ra, the sun god, decreed that Nut not give birth "any day of the year"
- Geb, god of the earth
- Geb & Nut had four children:
- Osiris, king of the earth
- Isis, his queen
- Set, god of chaos
- Nephthys, goddess of the dead
- Atum coughed up or spat out:
Osiris, Isis & Set origin of Egypt myth[edit | edit source]
- in the Egyptian origin myth
- Osiris is god and ruler of Egypt
- Isis is his wife
- Set is his brother, and god of the desert
- jealous of Osiris, Set murders Osiris and spreads his body parts across Egypt
- Isis flies across Egypt and reassembles Osiris, bringing him back to life
- since he already died, Osiris becomes ruler of the afterlife, god of the dead
- Isis becomes a symbol of the passing into eternal life
“The blood of Isis, the charms of Isis, the power of Isis are a protection unto me.”
- Set continues to rule Egypt until
- Horus, son of Osiris and Isis, defeats him and becomes ruler of Egypt
The Afterlife[edit | edit source]
- Book of the Dead
- sources:
- The Papyrus of Nes-min: an Egyptian Book of the Dead from the Detroit Institute of Arts
- Book of the Dead (wikipedia)
- The Book of the Dead by Tour Egypt
- Papyrus of Hunefer from the British Museum
- sources:
- other funerary texts & spells
- << to do
Priests[edit | edit source]
- sources of power
- priestly rule
Mummification[edit | edit source]
- bulleted info
- bulleted info
- bulleted info
- bulleted info
Mythology & Gods[edit | edit source]
Sun God: Amon-Re (ah-mun ray) Pharaoh connect to Amon-Re
notes to do:
- bulleted info
- bulleted info
- bulleted info
- bulleted info
Egyptian Gods:
Uncertainty vs. Regularity
water, sun, weather
Idolatry >> use the Maya book as example
>> used the idols to regularize the rains
fertility:
land and people
Nile: Egyptian self-conception Earth is flat, oval... the Nile marks its extent ... mountains beyond the known limits, with the “Heavenly River” on the other side ... Heavenly Boat... carried Sun-God “sat” (?)... sailed around the earth every day, using the “heavenly river” to get around nighttime... sunset = Heavenly Boat launched .. never knew the source of the Nile...thought it was fed by the Heavenly River, far to the south... ... Nile = life giving... came from a god who fed the water at its source in the Heavenly River
Egyptian Religion/ Gods Cycle of the day Day = life Night = death who can make the journey... passage from one world to the other Sun >> sun sets, goes into underworld >> passes through it and comes back into the living >> pushed across the sky by Khepri
Solar Barge: Boat that carried Ra through the underworld (night) Various gods traveled with him: Maat = order, opposite of chaos Thoth = moon, at the helm, steering Horus - sky God, depicted as a falcon
Death: - soul ferried across “lake of fire” to Osiris - Osiris weighed the heart against the “feather of truth” - sinners >>fed to the crocodile-shaped “Eater of the dead” - virtuous: go to “Happy Field of Food” for eternal life - “Book of the Dead” >>spells, charms, etc. “Negative Confession” to repeat to Osiris: see p. 29 � Mummification: not so much to use the body parts but to prove the divinity of the gods >>gods died >>see Golden Bough >>the heart = most important body part-- mind and soul
>>important to protect tombs, so that the soul could survive >> part of why they abandoned the pyramids
Ka = spirit
Ra (or Re) Sun god his eye in stone/gems was placed over the entrance wound to the mummified pharaohs .. rode the golden boat across the sky ... asp = symbol of Ra’s destructive power .. greatest temple at Thebes.. to Amon-Ra
Thoth god of intelligence and wisdom invented writing, math and sciences measured the flood of the Nile and movements of moon and starts
crocodile = evil scarab: good luck symbol cat = sacred, to kill one was damnation Bull Apis: represented the Nile >lived at Memphis in a stable attached to a temple
Phoenix the firebird w/ gold/red plumage at end of life-cycle, burns itself in cinnamon twigs new phoenix arises from the ashes
>> the phoenix may come from the origin myth
Amon-Re (Amun-Ra) later version of Ra/Re temple built by Ramses II at Karnak... used in James Bond movie Pharaohs linked to Amon-Re
Khepri lesser god who pushed the sun across the sky
Osiris ....
God who ruled Egypt until cast into the underworld by bro Set in pieces across Egypt
Isis put him together, but he could no longer rule the living
Became the God of the underworld, of death
God of the Nile
promised the afterlife
Isis goddess who ruled Egypt with Osiris Gave Osiris eternal life by putting him back together 1st taught women to grind corn, spin flax, weave cloth promised the afterlife
Set - originally god of the desert - associated with sandstorms and desert caravans - was god of Lower Nile... conflicted with God of Upper Nile, Horus (not yet son of Osiris) - Hyksos adopted Set - killed his brother Osiris - Set was the chosen god fo the Hyksos ... so the Egyptians turned against him in their mythology - Horace ripped off one of his testicles ... after trying to rape him
Horace (Horus) son of Osiris and Isis... avenged them and killed Set see above the “Solar Barge”
Anubis
- Jackel-headed god of the dead
- God of the dead
- jackals and dogs loitered at the edge of the desert, where the Egyptians buried their dead... they tried to protect the dead from the animals... created the God Anubis to protect against the jackels
- after rise of Osiris/Isis... Anubis becomes gatekeeper of the underworld... he measured the heart...and protected souls through their journey
- became god of the dying, and of embalming
Aton derived from Amon-Re monotheism by Akhenaton and Nefertiti Akhenaton = “he who serves Aton” 1380 bc - priests were unimpressed
Daily Life[edit | edit source]
- bulleted info
- bulleted info
- bulleted info
- bulleted info
- Famines and Plagues
Social, Political and Economic Structures[edit | edit source]
Government[edit | edit source]
- pharaoh political and military leader
- viziers, or high ministers/ officials, oversaw the government for the pharaohs
- see wikipeida entry for viziers here
- taxation based on agricultural production and excise taxes on trade
- sources:
- The ancient Egyptian administration from www.reshafim.org
Social Structures[edit | edit source]
- social class distribution not a strict pyramid (slaves at bottom of social structure did not constite a large portion of the population, which was distributed as per:
- gods
- ruling dynastic family
- priests
- nobles and nomarchs (rulers of nomes)
- merchant class
- military class
- artisans
- peasants
- slaves
- 9/10ths of population were peasant farmers, with economic rights and access akin to serfdom
- land belonged to the gods, which meant that the pharaohs were its caretakers
- land distribution a great power of the pharaohs (and weakness when land control was asserted by local rivals)
- priests and nobles controlled great tracts of land
Economy[edit | edit source]
- principal products & industry
- bread basket: Egyptian wealth was derived from its tremendous and diverse agricultural production
- linen industry based upon flax, a fibrous plant, which also yields flax oil
- ship building, including
- reed boats
- see [Khufu ship (wikipedia)] and [of the Two Lands (ship) (wikipedia)] from 2613 under Seneferu (fist ship to bear a name)
- reed boats


Ancient Egyptians were the first to document tools for ropemaking - ropes from papyrus (see [Rope and Knots in Ancient Egypt]
- sail construction from flax
- livestock, especially in Delta region
- mining of regional areas, especially the mountains to the East of the Nile
- exotic animals, ebony and ivory from African interior
- Egyptian trade extent
- across north, upper Nile, and East Africa
- the Mediterranean Sea, especially Crete, Phoenicia, and Cyprus
- Levant (Mediterranean coast of west Asia), Mesopotamia and and Indus India via Persian gulf trade routes
- Red sea trade routes, including Arabia and the Horn of Africa
- Egyptian shipping was not confined to the Nile, but for the most part, trade came to Egypt and not the other way around
- characteristics
- no coinage
- trade was sanctioned by the state (control) and taxed
- barter system based on weights and measures (no coinage), usually in gold, silver, copper, and gems
- the deben was the primary unit of value
- equivalent to about 90 grams of copper
Click EXPAND for description of the value and use of the deben by James C. Thompson:
- James C. Thompson writes:
Since seventy-five litters of wheat cost one deben and a pair of sandals also cost one deben, it made perfect sense to the Egyptians that a pair of sandals could be purchased with a bag of wheat as easily as with a chunk of copper. Even if the sandal maker had more than enough wheat, she would happily accept it in payment because it could easily be exchanged for something else. The most common items used to make purchases were wheat, barley, and cooking or lamp oil, but in theory almost anything would do.Source: [Ancient Egyptian Agriculture (Ancient History Encyclopedia)]
- principal imports:
- cypress trees from Lebanon (Phoenician trade)
- copper from Cyprus, tin from Syrian
- dyes from Phoenicia, especially purple dye
- myrrh from lower Arabia
- stones, gems, & minerals from Africa, Mesopotamia, Asia Minor, Greece, and Indus (lapis lazuli)
- animal skins, bones, etc. from across Africa
- sources:
Culture and Cultural & Technological Achievements[edit | edit source]
- world's earliest calendar started in Egypt at the year 4241 BC
- Egyptian calendar was unique as a solar and not lunar calendar
- Egyptian calendar shows stability and regularity of the Egyptian world
- first water clock built by Egyptians (during reign of Thutmose I (1526–1506 BC)
- mathematics developed as irrigation and crops develop
- writing system & paper
- influenced regional writing developments
- some speculation as to relationship between Hebrew and Egyptian writing
- sources?
- some speculation as to relationship between Hebrew and Egyptian writing
- influenced regional writing developments
- forms of writing
- names we used given by Greeks
- hieroglyphics
- = "sacred writing" or "sacred engraved signs"
- heiratic
- = "priestly writing"
- demotic
- = >> todo
- lines and dots: simplified heiratic
- Rosetta Stone
- papyrus paper: = earliest paper in the world
>> daily life here?
>> see articles used in WH Fall2011 >> drinking wine etc.
Literature[edit | edit source]
- Papyrus of Nes-min >> todo
- The Book of Am-Tuat: "That Which Is In the Afterworld"
- Amduat "That which is in the afterworld" wikipedia entry
- Egyptian funerary texts Wikipedia category list
- The Palermo Stone (pdf file)
- Old Kingdom kings list, shows Menes being conferred kingship by the god Horus; this text was used by Manetho
- see also Palermo Stone
- Abydos King List and Abydos King List (wikipedia)
Mathematics[edit | edit source]
- extensive, organized agricultural land use required that the ancient Egyptians develop practical geometry and other mathematical calculations
- additionally, cultural and religious focus on tracking the the sun and stars required complex mathematical calculations
- these mathematical skills were applied to Egyptian architecture, which was planned using precise mathematical measurements and calculations.
- math types included
- addition/ subtraction/ multiplication
- fractions
- geometry, esp. for calculating surface area and volume of 3-diminensial structures (architecture and engineering)
- algebra, including quadratic equation
Numeric system[edit | edit source]
- surviving evidence shows Egyptians used base-10 numeric system
- large dimensions, such as land or buildings, were measured in "cubits"
- had a script to display fractions
- including to use variables, such as 2/n, in unit fractions
- see Rhind Mathematical Papyrus - Wikipedia
- the number 276 would be represented as:

addition and subtraction[edit | edit source]
- like many early peoples, Egyptians recorded addition and subtracting using indicators of adding to or taking away numbers
- to add a number would be
- 2 <-- 1 = 3
- = adding 1 to 2
- Egyptian symbol for addition = "go in"
- 2 <-- 1 = 3
![]() (= feet walking towards the first number being added to)
(= feet walking towards the first number being added to)
so 1 ![]() 2 = 3
2 = 3
- to subtract a number would be
- 3 --> 1 = 02
- = taking away 1 from 3
- Egyptian symbol for subtraction = "go out"
- 3 --> 1 = 02
so 3 ![]() 1 = 2
1 = 2
![]() (= feet walking away from first number being added to)
(= feet walking away from first number being added to)
Gender equality[edit | edit source]
- women held higher status in Egyptian society than most other ancient civilizations
- due in part to Egyptian isolation, which lessened need to protect women from foreign invaders
- Female rulers
- see [Hatshepsut] wikipedia entry with list of Female Egyptian rulers
- women held higher status in Egyptian society than most other ancient civilizations
Slavery[edit | edit source]
- like most slavery, Egyptian slavery consisted primarily of conquered peoples
- the bulk of Egyptian labor was farmers who were employed for public works and warfare during the flooding season
- the Old Kingdom Palermo Stone states that the pharaoh Sneferu raided Nubia and brought back to Egypt 7,000 slaves; he also took 11,000 prisoners and 13,100 cattle from raids in Libya (see Sneferu
Historiography of Egypt[edit | edit source]
Egyptology[edit | edit source]
- study of ancient Egypt (see wikipedia entry here)
- ancient Egypt history unclear due to problems with sources
- timelines are especially difficult to confirm
- wikipedia "Conventional Egyptian chronology"
- wikipedia "Egyptian chronology" - this page discusses the problems in establishing Egytian chronologies
Egyptian archaeological record[edit | edit source]
- not always reliable: often works of state propaganda
- extensive gaps occur between surviving records
- Egyptian year count based on events and pharaohs which is difficult to translate to modern dating
Egyptian timeline via celestial dating[edit | edit source]
- using the path of the Dog Star, Sirius, Egyptologists have been able to correlate the position of the star with the ancient Egyptian calendar
- since the Egyptian calendar was the basis of the Roman calendar
- (which is the basis of the modern European "Gregorian" calendar)
- knowing that July 19 is the Egyptian date for the rise of Sirius, the Dog Star
- by matching surviving Egyptian records, astronomers and mathematicians were able to date the
- start of the 12th dynasty at 2000 BC
- start of the 18th dynasty at 1580 BC
- more or less by 3 years
- these calculations have allowed for accurate extrapolation of Egyptian records into modern dating
- they also showed the Manetho's timeline was greatly exaggerated
- by matching surviving Egyptian records, astronomers and mathematicians were able to date the
Manetho of Sebennytus[edit | edit source]
- Egyptian high priest (of the sun god Ra) who lived under the Greek king of Egypt, Ptolomey I
- lived either in late 3rd century (early 300s) to early 2nd century B.C. (300s-200s BC)
- the name "Menotho" may mean "Truth" or "Gift" of "Thoth" (Egyptian god of the moon, knowledge, writing)
- major work is "Aegyptiaca," the first organized historical overview of ancient Egypt, completed in 271 BC
- Aegyptiaca = "History of Egypt"
- Kings List: of rulers and gods who ruled before the kings
- kings list was an Egyptian tradition: see Saqqara Tablet
- the list of ruling "dynasties" comes to us from Manetho
- includes narratives of events across Egyptian history
- written in Greek, most of original is lost
- historians rely on translations by others, notably Josephus, Africanus, and Eusebius, all from the Roman era
- see essay by John Dillery, The First Egyptian Narrative History: Manetho and Greek Historiography
In the early 3rd century BC, during the reign of Ptolemy II Philadelphus, the Egyptian priest Manetho of Sebennytus wrote a history of his native land in the Greek language. The work is clearly indebted both to Egyptian and Greek texts. Its importance cannot be over stressed: two cultures, and the narrative systems they employed, were brought together in the composition of his Aegyptiaca, or Egyptian Matters. Issues such as the impact of Greek historical writing on Egyptian conceptions of the past, the intended audience of such a work, and the role of the native elite in the Macedonian and Greek governance of Egypt are all opened up through Manetho's work.
- sources:
- (wikipedia entry on Manetho here
- The First Egyptian Narrative History: Manetho and Greek Historiography - Academic article
- Manetho's "Aegyptiaca" - images of surviving manuscript
Herodotus "Histories"[edit | edit source]
- Herodotus of Halicarnassus wrote "Histories", which included a study of Egypt
- Book 2 contains three chapters with subsections:
- Fourth logos: Geography of Egypt
- Fifth logos: customs and animals of Egypt
- Tyre
- Egyptian customs
- The hippopotamus
- Mummification
- Sixth logos: history of Egypt
- text: The relief of Sesostris
- for Herodotus's text see:
- AN ACCOUNT OF EGYPT BY HERODOTUS BEING THE SECOND BOOK OF HIS HISTORIES CALLED EUTERPE (Gutenburg)
- Herodotus' Histories (livius.org) provides commentary about each book of Herodotus
Other Histories and ancient visitors[edit | edit source]
- Hecataeus of Miletus, 6th century B.C.
- called, "the father of Geography," a Greek diplomat and philosopher from 6th century BC who had visited Egypt with the Persian court after its conquest of Egypt
- wrote "Journey round the Earth" or "World Survey"
- survive only in fragments (pieces) or citations from later authors
- Herodotus relied on Hecataeus
- Abd al-Latif al-Baghdadi, 14th century AD Islamic traveler and writer
- visited Egypt and wrote in wonder of the ancient monuments
- wrote "An Account of Egypt"
- importantly promoted the study and preservation of the archaeological remains in Egypt
European "Egyptologists"[edit | edit source]
- following early 19th century French invasion of Egypt, the land was opened up to European visitors
- especially under later British rule, historians investigated the ancient archeology and texts and translated earlier texts from the Greeks, especially
Ancient Egypt Vocabulary[edit | edit source]
- black land / red land
- pharaoh: great house
- vizier
- regent
- >> to build
External Resources[edit | edit source]
Websites[edit | edit source]
- Ancient Egypt Ancient Egypt (wikipedia)
- Ancient Egypt (simple wikipedia
- Tour Egypt has a variety of useful articles on Ancient Egypt that include bibliographies
- British Museum Ancient Egypt pages with student readings and easy to read content material
- Digital Egypt for Universities
- detailed timeline from Answers.com
- Egypt's Goldent Empire by PBS
- Guide to the World of the Ancient Egyptians
- The Ancient Egypt Site (with link to Facebook page)
Articles[edit | edit source]
See Also[edit | edit source]
- bulleted link to other related internal or web articles
- bulleted link to other related internal or web articles
Ancient Egypt in modern popular culture[edit | edit source]
- Steve Martin, SNL "King Tut" skit & dance
Lesson Plans & Teaching Ideas[edit | edit source]
See Essential Questions << link
Egypt Main ideas for students[edit | edit source]
- role of geography
- Nile as source of life, center of cosmos
- role of wild animals in Egyptian identity & religion
- desert as yin/yang to Nile
- climate role in mummification
- role of Nile as movement:
- Egypt easy to unify, hard to conquer
- control of joining point of Upper/Lower Egypt = control of commerce, taxation, and movement in Egypt
Other Student Projects and Investigations[edit | edit source]
- Evaluate why did Thutmose III and his son erase Hatshepsut's legacy? What are the theories, what do you think?
- Why was Akhenaton unable to impose monotheism upon Egypt?
Readings for students[edit | edit source]
- Books:
- [1] "The Book of the Ancient World" by Dorothy Mills (1927, 2007 reprint) which has young reader level, descriptive and narrative stories about Ancient Egyptians (see especially the "A Visit to Thebes" chapter which describes a fictional visit to Egypt by a Phoenician trader and his son)
- "A History of Egypt From The Earliest Times To The Persian Conquest" by James Breasted, 1905 (archive.org)
- Web collections:
- https://www.pbs.org/empires/egypt/index.html "Egypt's Golden Empire" (PBS.org on the New Kingdom)]
- tomb inscriptions can be especially revealing; some that are accessible to students include:
- Ptah-Hotep entry from AAA Encyclopedia with "the Instruction of Ptah-Hotep"
- Papyrus of Ani with the Spell of Maat (wikipedia) - the "Forty-Two Declarations of Purity" make interesting reading for students to evaluate Egyptian faith and everyday life