English language: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
English originated in Anglo-Saxo | |||
See also [[Language and etymology]] | |||
== Word parts & types == | |||
=== lexemes === | |||
* noun, verb, adjective and adverb "stems" (basic word by itself | |||
=== morphemes === | |||
* sounds that are added to lexemes to create new words | |||
** including prefixes, suffixes and stem changes | |||
*** ''pre-, -ly, -en, -s'' | |||
== English word origin == | == English word origin == | ||
[[Image:Old norse, ca 900.svg|right|350px|thumb| | |||
[[Image:Old norse, ca 900.svg|right| | |||
The approximate extent of Old Norse and related languages in the early 10th century:<br> | The approximate extent of Old Norse and related languages in the early 10th century:<br> | ||
<span style="color:#fff; background:#ff0000>Old West Norse dialect</span><br> | <span style="color:#fff; background:#ff0000>Old West Norse dialect</span><br> | ||
<span style="color:#fff; background:#ff9933>Old East Norse dialect</span><br> | <span style="color:#fff; background:#ff9933>Old East Norse dialect</span><br> | ||
<span style="color:#fff; background:#ff00ff>Old Gutnish dialect</span><br> | <span style="color:#fff; background:#ff00ff>Old Gutnish dialect</span><br> | ||
<span style="background:#ffff00>Old English</span><br> | <span style="color:#000; background:#ffff00>Old English</span><br> | ||
<span style="color:#fff; background:#0000ff>Crimean Gothic</span><br> | <span style="color:#fff; background:#0000ff>Crimean Gothic</span><br> | ||
<span style="color:#fff; #00ff00>Other Germanic languages with which Old Norse still retained some mutual intelligibility</span>]] | <span style="color:#fff; #00ff00>Other Germanic languages with which Old Norse still retained some mutual intelligibility</span>]] | ||
==== Angles / Anglo-Saxon ==== | |||
* from the Angles, a Germanic peoples who migrated to the British Islands in the 400s-600s AD. | |||
** part of the Anglo-Saxon invasions | |||
* English is one of the "Anglo-Frisian" languages | |||
==== Language origins of Modern English ==== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+Origins of Modern English | |||
!Germanic | |||
!Old French | |||
!Latin | |||
!Greek | |||
!Other | |||
!Proper Names | |||
|- | |||
|26% | |||
|29% | |||
|29% | |||
|6% | |||
|6% | |||
|4% | |||
|} | |||
== The most common words in English== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+ Top Ten Most Common Words in English | |||
|1) the | |||
|(article) | |||
| 6) in | |||
|(preposition) | |||
|- | |||
| 2) be | |||
|(verb) | |||
| 7) that | |||
|(relative pronoun, dependent marker) | |||
|- | |||
|3) to | |||
|(particle, preposition) | |||
|8) have | |||
|(verb) | |||
|- | |||
|4) and | |||
|(conjunction) | |||
|9) I | |||
|(pronoun) | |||
|- | |||
|5) a | |||
|(article) | |||
|10) it | |||
|(pronoun) | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
== English | == English synonymous & part of speech word use== | ||
*the English language has a huge number of words that have multiple definitions | |||
*other languages may be more explicit with distinct words that English will cover with a single word. | |||
*for example: | |||
==English words & parts of speech distribution== | |||
* English contains | *English contains about 600,000 words | ||
** when | **as counted by the Oxford English Dictionary, there are 171,476 words in current use and 47,156 obsolete words | ||
***the Dictionary also counts 250,000 "distinct" words, excluding inflections (word ending changes) | |||
**when word definitions are counted, English has 1,402,895 words | |||
***i.e., the word "love" generally has five definitions in the dictionary | |||
**when counting "headwords" and "lemmas" (words produced from a headword), English has 578,707 words | |||
***"headword" = a word from which other words are derived, such as "break > broken > broke | |||
**see | |||
***[https://web.archive.org/web/20170909203258/https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/explore/how-many-words-are-there-in-the-english-language How many words are there in the Engli... | Oxford Dictionaries (archive.org)] | |||
***[[wikipedia:Corpus_linguistics#English_corpora|Corpus linguistics - Wikipedia]] | |||
***[https://www.babbel.com/en/magazine/language-most-words Which Language Has The Most Words? (babbel.com)] | |||
***[[wikipedia:List_of_dictionaries_by_number_of_words|List of dictionaries by number of words - Wikipedia]] | |||
===Parts of Speech frequency as percent of all words=== | |||
===parts of speech as percentage of all words=== | |||
*in general, English consists of | |||
**Adjectives: 25% | |||
**Nouns: 50% | |||
**Verbs: 7% | |||
***see: [https://www.alphadictionary.com/articles/oed.html#:~:text=Subtracting%20the%20archaic%20words%20leaves%20us%20with%20about,made%20up%20of%20interjections%2C%20conjunctions%2C%20prepositions%2C%20suffixes%2C%20etc. How Many Words are in the Oxford English Dictionary? * alphaDictionary] | |||
===parts of speech as percentage of word usage, conversational v. formal/academic: === | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ English Language Percent Frequency of Use of Parts of Speech | ||
! | |||
!Adjectives | !Adjectives | ||
!Adverbs | !Adverbs | ||
!Conjunctions | |||
!Determiners | |||
!Nouns | !Nouns | ||
!Prepositions | !Prepositions | ||
!Pronouns | |||
!Verbs | !Verbs | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |Conversational | ||
|2.5% | |||
|5% | |||
|4.5% | |||
|4.5% | |||
|15% | |||
|5.5% | |||
|16.5% | |||
|12.5% | |||
|- | |||
|Formal/ Academic | |||
|10% | |||
| 3% | |||
| 5% | |||
|10% | |||
|30% | |||
|15% | |||
|4% | |||
|10% | |||
|- | |||
| | | | ||
| | |Adjectives | ||
|Adverbs | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|Nouns | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|Verbs | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 36: | Line 153: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 44: | Line 159: | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
*source: [https://ginsengenglish.com/blog/parts-of-speech-in-english#:~:text=Take%20a%20look%20at%20the%20following%20table%20showing,to%20give%20a%20general%20sense%20of%20the%20proportions. The 9 Parts of Speech in English | Ginseng English] (from Biber, et. al., (1999). ''Longman Grammar of Spoken and Written English.)'' | |||
[[Category:Language Arts]] | [[Category:Language Arts]] | ||
[[Category:Linguistics]] | [[Category:Linguistics]] | ||
[[Category:Language]] | [[Category:Language]] | ||
[[Category:History of language]] | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
Latest revision as of 16:27, 1 March 2024
English originated in Anglo-Saxo
See also Language and etymology
Word parts & types[edit | edit source]
lexemes[edit | edit source]
- noun, verb, adjective and adverb "stems" (basic word by itself
morphemes[edit | edit source]
- sounds that are added to lexemes to create new words
- including prefixes, suffixes and stem changes
- pre-, -ly, -en, -s
- including prefixes, suffixes and stem changes
English word origin[edit | edit source]
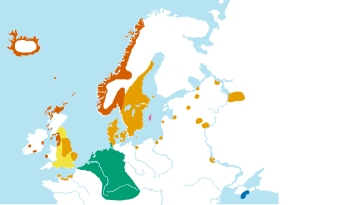
Old West Norse dialect
Old East Norse dialect
Old Gutnish dialect
Old English
Crimean Gothic
Other Germanic languages with which Old Norse still retained some mutual intelligibility
Angles / Anglo-Saxon[edit | edit source]
- from the Angles, a Germanic peoples who migrated to the British Islands in the 400s-600s AD.
- part of the Anglo-Saxon invasions
- English is one of the "Anglo-Frisian" languages
Language origins of Modern English[edit | edit source]
| Germanic | Old French | Latin | Greek | Other | Proper Names |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26% | 29% | 29% | 6% | 6% | 4% |
The most common words in English[edit | edit source]
| 1) the | (article) | 6) in | (preposition) |
| 2) be | (verb) | 7) that | (relative pronoun, dependent marker) |
| 3) to | (particle, preposition) | 8) have | (verb) |
| 4) and | (conjunction) | 9) I | (pronoun) |
| 5) a | (article) | 10) it | (pronoun) |
English synonymous & part of speech word use[edit | edit source]
- the English language has a huge number of words that have multiple definitions
- other languages may be more explicit with distinct words that English will cover with a single word.
- for example:
English words & parts of speech distribution[edit | edit source]
- English contains about 600,000 words
- as counted by the Oxford English Dictionary, there are 171,476 words in current use and 47,156 obsolete words
- the Dictionary also counts 250,000 "distinct" words, excluding inflections (word ending changes)
- when word definitions are counted, English has 1,402,895 words
- i.e., the word "love" generally has five definitions in the dictionary
- when counting "headwords" and "lemmas" (words produced from a headword), English has 578,707 words
- "headword" = a word from which other words are derived, such as "break > broken > broke
- see
- as counted by the Oxford English Dictionary, there are 171,476 words in current use and 47,156 obsolete words
Parts of Speech frequency as percent of all words[edit | edit source]
parts of speech as percentage of all words[edit | edit source]
- in general, English consists of
- Adjectives: 25%
- Nouns: 50%
- Verbs: 7%
parts of speech as percentage of word usage, conversational v. formal/academic:[edit | edit source]
| Adjectives | Adverbs | Conjunctions | Determiners | Nouns | Prepositions | Pronouns | Verbs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conversational | 2.5% | 5% | 4.5% | 4.5% | 15% | 5.5% | 16.5% | 12.5% |
| Formal/ Academic | 10% | 3% | 5% | 10% | 30% | 15% | 4% | 10% |
| Adjectives | Adverbs | Nouns | Verbs | |||||
- source: The 9 Parts of Speech in English | Ginseng English (from Biber, et. al., (1999). Longman Grammar of Spoken and Written English.)
| |}