Geography vocabulary
Geography Vocabulary [category:Geography] [category:Social Studies] [category:Social Studies Skills]
- code for EXPAND/COLLAPSE functions:
code: <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:50%"> text * for bullets * '''>''' for bullets with bold </div> * Click EXPAND to see list of important >>
Five Themes of Geography[edit | edit source]
- Location
- Absolute Location
- Relative Location
- Regions
- Place
- Movement
- Human-Environment Interaction (Relationships within Places)
- Cultural Diffusion
- See Social Studies Skills
Map terminology[edit | edit source]
- Latitude
- Longitude
- Equator
- Prime Meridian
- International Dateline
- Meridians
- Parallels
- a.m. / p.m.
- equinox
- solstice
- Tropic of Cancer
- Tropic of Capricorn
Physical Geography[edit | edit source]
- the study of the elements that constitute the earth's surface and how they interact
- includes meteorology, which is the study of weather and weather prediction
- [Physical geography(wiki)]
Water bodies[edit | edit source]
bay[edit | edit source]
canal[edit | edit source]
- man-made straits that connect two larger bodies of water
- canals provide important water passage to connect water bodies that would otherwise require long-distance water travel around land bodies or continents
- usually canals are built across isthmuses
- Click EXPAND to see list of important canals
channel[edit | edit source]
- synonymous with "strait" but usually referring to a smaller or less important strait
- see strait below
delta[edit | edit source]
gulf[edit | edit source]
lake[edit | edit source]
ocean[edit | edit source]
sea[edit | edit source]
strait[edit | edit source]
- a narrow body of water that connects larger bodies of water, or, a narrow channel that separates land masses
- synonymous with channel, passage, or pass
- implicit in the terminology is that the strait allows for navigation, or passage, from one larger body of water to another
- "strait comes from Old French "estreit" for "tight" or "narrow"
click EXPAND to see list of important straits:
river[edit | edit source]
- rivers flow downhill, usually but not always into an ocean
- upstream v. downstream
- tributary
- estuary
- Gulf of Ob
- world's longest estuary
- fed by the Ob River and feeding into the Kara Sea (part of the Arctic Ocean)
- delta
- silt
- flow & discharge
- measurement of the amount of water a river carries
- Ten longest rivers in the world
- note: there is always a dispute over these lists as to the exact measurement
- this list is derived from ** See [of rivers by length (wiki)]
- which measures total length of river systems (i.e., includes tributaries)
- Click EXPAND to see list of the ten longest rivers
stream[edit | edit source]
oasis[edit | edit source]
- See Ancient Egypt outline
See also:
- Hydrology / water cycle
atmosphere[edit | edit source]
winds[edit | edit source]
- Trade winds: blow from east to west (generally)
- Westerlies: blow from west to east (generally
- these winds defined oceanic travel during the "age of sail" (wind-powered boats)
- they also defined location and direction of European expeditions during the Age of Discovery
- ex. the Portuguese discovered Brazil because their ships had to sail west, across the Atlantic in order to catch the winds and currents that would then carry their ships south and east to cross the Cape Peninsula and the Cape of Good Hope (southern tip of Africa)
- windward v. leeward
- windward = upwind, or that side facing or nearest to the incoming wind
- leeward = downwind, or that side facing away or furthest from the incoming wind
- see the Lesser Antilles for the "Leeward" and "Westward" Islands
Land forms[edit | edit source]
archipelago[edit | edit source]
- a series of geographically proximate or geologically similarly island, usually formed in a chain or a cluster
basin[edit | edit source]
butte[edit | edit source]
cape[edit | edit source]
- a "headland", "promontory" or large body of land that extends into a larger water body, usually an ocean or a sea
- "headland" is a "coastal landform," usually with a high point and cliffs
- "promontory" is a raised land body that extends into lower land or water
- promontories are often used a defensive positions for forts, castles and defensive positions
- a promontory in water is a peninsula
- Click EXPAND for a list of important capes:
canyon[edit | edit source]
- a "cleft" or opening with steep cliff walls on either side
- canyons are usually formed by erosion from rivers
- but can also be caused by "weathering" (see definition under geology entry)
- also called a gorge

- narrows or slot canyon is a very narrow canyon and can extend for some distance
- see "The Subway," a slot canyon in Zion National Park, Utah
continent[edit | edit source]
- largest continuous unit of a land form or land mass
- * except for Europe (and, thus Asia), continents have defined perimeters
- continents are defined by extent, separation, tectonic plates (some have multiple plates)
- click on EXPAND to see list of Continents
- disputed continents
- Australia
- sometimes considered world's largest island
- Europe
- Europe is technically not a continent, but if so, neither is Asia
- considered together, Europe + Asia = "Eurasia"
- the concept of Europe as a continent is traditional and cultural, but still valid geographically
- Europe is technically not a continent, but if so, neither is Asia
- click EXPAND for more on definition of Europe as a continent
gorge[edit | edit source]
- another name for canyon (see above)
hill[edit | edit source]
island[edit | edit source]
isthmus[edit | edit source]

- land-form that has large water bodies on opposite sides
- and connects two larger land forms
- also called a "land bridge"
- plural form = "isthmuses"
- examples:
- Karelian Isthmus << connects Russia to Finland
- Kra Isthmus << connects southeast Asia to the Malay peninsula
- Panama << connects North and South Americas
- Sinai << connects northeast Africa to southwest Asia
- canals are usually built across isthmuses
- Panama Canal
- Corinth Canal
- Suez Canal
land-bridge[edit | edit source]
mountain[edit | edit source]
peninsula[edit | edit source]
plateau[edit | edit source]
tectonic plates[edit | edit source]
trench[edit | edit source]
- trench
- a large, narrow (as compared to length) depression in the ground or underwater
- trenches are caused by erosion, glaciers, or movement of tectonic plates
- trenches can be on land or under water, such as the Mariana trench, deepest
- smaller forms of a trench are called a "gully" or a "ditch"
- larger trenches caused by tectonic plate movements are also called "rift valleys"
- volcano
volcano[edit | edit source]
- Sources:
- [Landform (National Geographic)]
Major world regions[edit | edit source]

- major regions
- there are many regions and sub-regions and different sources will define these regions differently
- the United Nations uses "geoscheme" system to define major world regions
- we will list these regions per continent
- See [List of Physiographic Regions per continent (wiki)]
Americas[edit | edit source]
- North America
- Central America
- South America
- Caribbean
Asia[edit | edit source]
- Central Asia (Russian Asia, Mongolia)
- East Asia (China, Korea, Japan)
- South Asia (Indian sub-continent)
- Southeast Asia (Vietnam, Thailand, Malyasia, Indonesia, etc.)
- West Asia (Middle East)
- Asia Minor, Anatolia
Africa[edit | edit source]
- East or Eastern Africa
- Horn of Africa = the peninsula of east Africa between the Red Sea and the Indian Ocean
- = the easternmost point of Africa
- Horn of Africa = the peninsula of east Africa between the Red Sea and the Indian Ocean
- North or Northern Africa
- South or Southern Africa (not the nation "South Africa")
- Sub-Saharan Africa
- West or Western Africa
Australia[edit | edit source]
Europe[edit | edit source]
- Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Scandinavia
Other major regions terminology[edit | edit source]
- Eurasia
- Mediterranean
- Latin America
World oceanic regions[edit | edit source]
- Mediterranean
- Arabian Sea
- Indian Ocean
- Atlantic Ocean
- Pacific Ocean
- Gulf of Mexico
- Caribbean Sea
- China Sea
- North Sea
- Macaronesia (Atlantic)
Oceania[edit | edit source]

- Oceania
- Pacific region in general, divided into
- Australasia
- Melanesia
- Micronesia
- Polynesia
- List of independent nations of Oceania:
- Click EXPAND to see list of independent nations of Oceana
- See [List of sovereign states and dependent territories in Oceania (wiki)]
Macaronesia[edit | edit source]
- island region in Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Portugal and West Africa
- volcanic islands
- Macaronesia consists of:
- Azores islands
- Portuguese territories
- Canary Islands
- Portuguese territories
- Madeira islands
- Spanish territories
- Cape Verde
- officially "Republic of Cabo Verde"
- it won independence from Portugal in 1975
- a democratic republic
- named for Cape Vert in Senegal, which is directly east of Cape Verde
- consists of 10 volcanic islands
- officially "Republic of Cabo Verde"
Climate[edit | edit source]
Climate Zones[edit | edit source]
see also : [Climate (Geography)]
- Roaring Forties
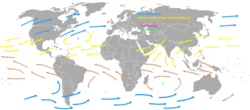

- westerly winds that cross from west to east along the southern hemisphere 40-50th parallels
- the Roaring Forties aided age of sail shipping routes from south of Africa to Australia
- and from Australia/New Zealand to the southern tip of South America
Geology & geological processes[edit | edit source]
Land forms processes[edit | edit source]
- erosion = the transport or movement of rocks and soil by water or wind
- erosion spreads silt (important for farming), forms canyons, coastlines, and other surface features
- types or causes of erosion:
- rivers
- rain/snow fall
- tides/waves
- atmospheric (wind, gasses)
- glaciers
- see [Erosion (wiki)]
- weathering = breakdown of rocks and soil from contact with water, the atmosphere, and organisms
- weathering is not erosion, as weathering does not include transit of rocks and soil
Hydrology cycle[edit | edit source]
Water forms processes[edit | edit source]
- waves = oscillations
- waves in water are technically "wind waves"
- water waves are caused by winds
- underwater waves
- ocean floor topography causes underwater waves
- highest underwater waves occur in the Luzon Strait between Taiwan and the Philippines
- caused by two parallel underwater ridges
- some underwater waves there can be as high as 1,600 feet
- see " Geoffrey Giller, “Long a Mystery, How 500-Meter-High Undersea Waves Form Is Revealed.” ©2014 by Scientific American
[edit | edit source]
Geography Fun Facts & Oddities[edit | edit source]
See also:
- [[Geography Bee
- Geography fun facts & oddities