Religion: Difference between revisions
(superstition) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Religion ''' | '''Religion ''' | ||
== | == Origins & cultural practice == | ||
=== Ritual === | === Explaining the world === | ||
* burial | |||
==== World and human origins ==== | |||
* Humans naturally want to know "why" | |||
* Why are we here? | |||
** religions and founding myths usually intersect | |||
* What is our purpose? | |||
** religions | |||
==== Purpose of life ==== | |||
* a primary function of religion is to order daily life | |||
* religion may guide | |||
** social structures | |||
** political structures | |||
** class, profession, and other hierarchies | |||
*** note that the word "hierarchy" originally means "rank in the sacred order" (see [https://www.etymonline.com/search?q=heirarchy| heirarchy word origin (etymonline)] | |||
==== Reflect or reinforce social structures ==== | |||
* religious belief provides authenticity and legitimacy to political, social and cultural systems or structures | |||
* ex.: | |||
** across human history, hereditary rule (especially monarchy) is the most stable political system | |||
*** because the "first born" of the ruler is selected by God/gods | |||
**** therefore the first born is legitimized by belief in that God/gods | |||
===Mitigating [[Uncertainty]]=== | |||
==== Ritual==== | |||
*burial | |||
* sacrifice | * sacrifice | ||
** purpose | **purpose | ||
** types of sacrifice | **types of sacrifice | ||
*** animal sacrifice | ***animal sacrifice | ||
*** human sacrifice | ***human sacrifice | ||
=== Superstition === | ==== Superstition==== | ||
* 13 and Friday the 13th superstitions | * 13 and Friday the 13th superstitions | ||
** many ancient counting systems, especially Babylonian, were 12-base | **many ancient counting systems, especially Babylonian, were 12-base | ||
*** therefore 13 marked a bad number | ***therefore 13 marked a bad number | ||
** in Christianity, Judas was considered the 13th disciple at the Last Supper | **in Christianity, Judas was considered the 13th disciple at the Last Supper | ||
*** since he betrayed Jesus, 13 is associated with him | ***since he betrayed Jesus, 13 is associated with him | ||
*** it is likely that the prejudice against pre-existed the story of the Last Supper and Judas | ***it is likely that the prejudice against pre-existed the story of the Last Supper and Judas | ||
* see: | *see: | ||
** [[https://www.history.com/topics/folklore/friday-the-13th Friday the 13th (History.com)]] | **[[https://www.history.com/topics/folklore/friday-the-13th Friday the 13th (History.com)]] | ||
== Prehistoric == | ==Prehistoric== | ||
* animism | *animism | ||
* polytheism | *polytheism | ||
=== Paleolithic === | ===Paleolithic === | ||
* conceptual thought | *conceptual thought | ||
* spirituality | *spirituality | ||
* examples | *examples | ||
** cave paintings | **cave paintings | ||
** pictograms | **pictograms | ||
** figurines | **figurines | ||
*** Venus figurine | *** Venus figurine | ||
*** lion man | *** lion man | ||
*** totemism | ***totemism | ||
=== Neolithic === | === Neolithic === | ||
* examples | *examples | ||
** ritual burial | **ritual burial | ||
** megaliths | **megaliths | ||
== Ancestor Worship == | ==Ancestor Worship== | ||
* Neolithic origins * | *Neolithic origins * | ||
* | * | ||
== Mythology == | ==Mythology== | ||
== Polytheism == | ==Polytheism== | ||
| Line 53: | Line 78: | ||
== Organized Religions == | == Organized Religions == | ||
* listed in approximate chronological order of development | *listed in approximate chronological order of development | ||
=== Hinduism === | ===Hinduism=== | ||
=== Zoroasterism === | ===Zoroasterism=== | ||
=== Bhuddism === | ===Bhuddism=== | ||
== Abrahamic religions == | ==Abrahamic religions== | ||
=== Judaism === | ===Judaism=== | ||
** Old Testament | **Old Testament | ||
=== Christianity === | ===Christianity=== | ||
**New Testament | **New Testament | ||
=== Islam === | ===Islam=== | ||
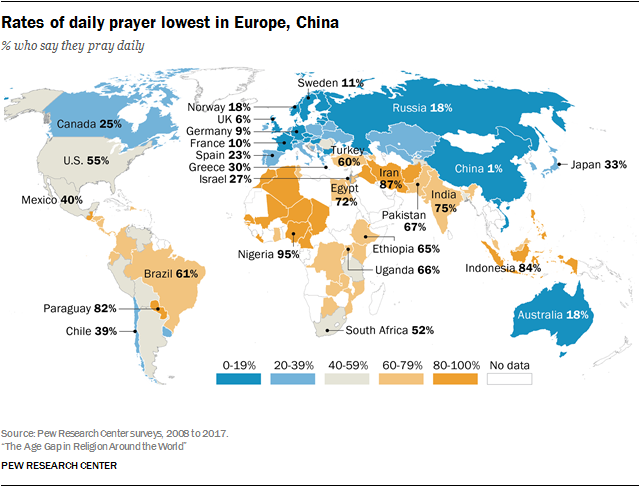
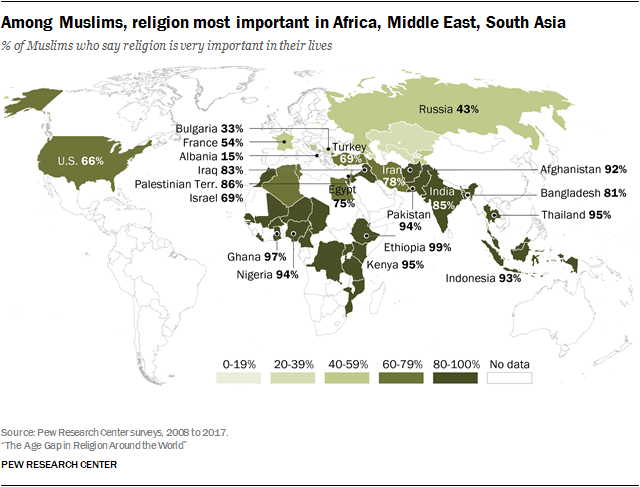
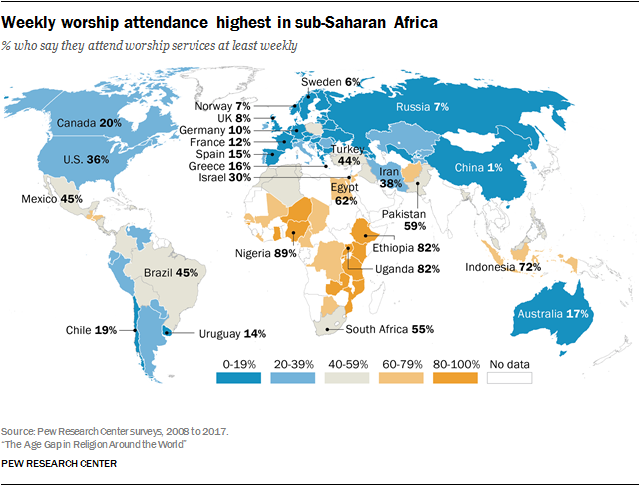
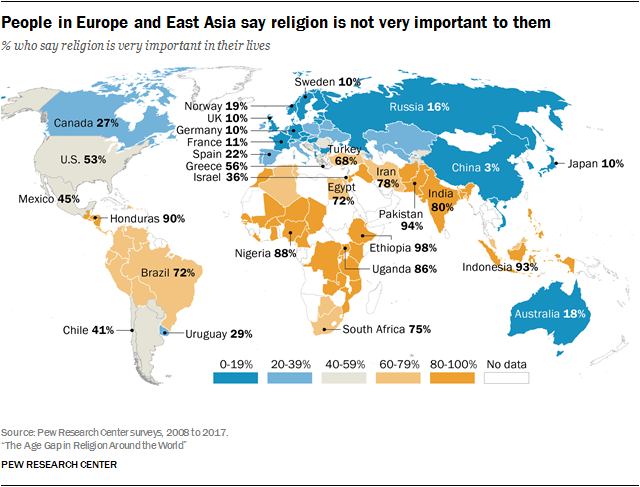
== Worldwide religiosity == | |||
=== Pew Research 2018 worldwide survey === | |||
* from [https://www.pewresearch.org/religion/2018/06/13/how-religious-commitment-varies-by-country-among-people-of-all-ages/|Pew Research: 3. HOW RELIGIOUS COMMITMENT VARIES BY COUNTRY AMONG PEOPLE OF ALL AGES] | |||
<html><a href="https://www.pewresearch.org/religion/2018/06/13/how-religious-commitment-varies-by-country-among-people-of-all-ages/pf-06-13-18_religiouscommitment-03-09/"><img src="https://www.pewresearch.org/religion/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2018/06/PF.06.13.18_religiouscommitment-03-09-.png?w=640"></a><a href="https://www.pewresearch.org/religion/2018/06/13/how-religious-commitment-varies-by-country-among-people-of-all-ages/pf-06-13-18_religiouscommitment-03-07/"><img src="https://www.pewresearch.org/religion/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2018/06/PF.06.13.18_religiouscommitment-03-07-.png?w=640"></a><br> | |||
</html> | |||
<br> | |||
<html><a href="https://www.pewresearch.org/religion/2018/06/13/how-religious-commitment-varies-by-country-among-people-of-all-ages/pf-06-13-18_religiouscommitment-03-08/"><img src="https://www.pewresearch.org/religion/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2018/06/PF.06.13.18_religiouscommitment-03-08-.png?w=639"></a><br> | |||
</html> | |||
<html> | |||
<a href="https://www.pewresearch.org/religion/2018/06/13/how-religious-commitment-varies-by-country-among-people-of-all-ages/pf-06-13-18_religiouscommitment-03-05/"><img src="https://www.pewresearch.org/religion/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2018/06/PF.06.13.18_religiouscommitment-03-05-.png?w=640"></a><br></html> | |||
*[[World Religions]] | *[[World Religions]] | ||
| Line 73: | Line 110: | ||
*[[Ethics & Morality]] | *[[Ethics & Morality]] | ||
==Teaching religion== | |||
*[[Religion Pedagogy & Teaching Strategies]] | *[[Religion Pedagogy & Teaching Strategies]] | ||
*Example of religious teaching: [https://wiki.rejoiceinmary.org Catholic Catechism (rejoiceinmary.org)] | |||
Revision as of 15:23, 19 February 2024
Religion
Origins & cultural practice[edit | edit source]
Explaining the world[edit | edit source]
World and human origins[edit | edit source]
- Humans naturally want to know "why"
- Why are we here?
- religions and founding myths usually intersect
- What is our purpose?
- religions
Purpose of life[edit | edit source]
- a primary function of religion is to order daily life
- religion may guide
- social structures
- political structures
- class, profession, and other hierarchies
- note that the word "hierarchy" originally means "rank in the sacred order" (see heirarchy word origin (etymonline)
Reflect or reinforce social structures[edit | edit source]
- religious belief provides authenticity and legitimacy to political, social and cultural systems or structures
- ex.:
- across human history, hereditary rule (especially monarchy) is the most stable political system
- because the "first born" of the ruler is selected by God/gods
- therefore the first born is legitimized by belief in that God/gods
- because the "first born" of the ruler is selected by God/gods
- across human history, hereditary rule (especially monarchy) is the most stable political system
Mitigating Uncertainty[edit | edit source]
Ritual[edit | edit source]
- burial
- sacrifice
- purpose
- types of sacrifice
- animal sacrifice
- human sacrifice
Superstition[edit | edit source]
- 13 and Friday the 13th superstitions
- many ancient counting systems, especially Babylonian, were 12-base
- therefore 13 marked a bad number
- in Christianity, Judas was considered the 13th disciple at the Last Supper
- since he betrayed Jesus, 13 is associated with him
- it is likely that the prejudice against pre-existed the story of the Last Supper and Judas
- many ancient counting systems, especially Babylonian, were 12-base
- see:
Prehistoric[edit | edit source]
- animism
- polytheism
Paleolithic[edit | edit source]
- conceptual thought
- spirituality
- examples
- cave paintings
- pictograms
- figurines
- Venus figurine
- lion man
- totemism
Neolithic[edit | edit source]
- examples
- ritual burial
- megaliths
Ancestor Worship[edit | edit source]
- Neolithic origins *
Mythology[edit | edit source]
Polytheism[edit | edit source]
Organized Religions[edit | edit source]
- listed in approximate chronological order of development
Hinduism[edit | edit source]
Zoroasterism[edit | edit source]
Bhuddism[edit | edit source]
Abrahamic religions[edit | edit source]
Judaism[edit | edit source]
- Old Testament
Christianity[edit | edit source]
- New Testament
Islam[edit | edit source]
Worldwide religiosity[edit | edit source]
Pew Research 2018 worldwide survey[edit | edit source]
Teaching religion[edit | edit source]
- Religion Pedagogy & Teaching Strategies
- Example of religious teaching: Catholic Catechism (rejoiceinmary.org)