Federalist No. 10: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
** Federalist no 9: '''The Utility of the Union as a Safeguard Against Domestic Faction and Insurrection''' (by Hamilton) | ** Federalist no 9: '''The Utility of the Union as a Safeguard Against Domestic Faction and Insurrection''' (by Hamilton) | ||
** Federalist no. 10: '''The Same Subject Continued: The Union as a Safeguard Against Domestic Faction and Insurrection''' (by Madison) | ** Federalist no. 10: '''The Same Subject Continued: The Union as a Safeguard Against Domestic Faction and Insurrection''' (by Madison) | ||
[[File:Federalist No 10 school4schools-wiki.jpg|thumb]] | |||
==Federalist No. 10 Summary == | ==Federalist No. 10 Summary == | ||
Revision as of 13:50, 4 May 2022
Understanding Federalist 10: translating the text & the big ideas
See also:
The Federalist Papers
- a series of 85 essays published in New York newspapers and distributed nationally in 1787-1788
- the essays explained and defended the proposed federal constitution of 1787
- which can be generally defined as creation of a new, centralized government under "republican" principles
- those being representation, separation of powers, and limits on the power of the majority
- which can be generally defined as creation of a new, centralized government under "republican" principles
- see here for audio book version of the Federalist papers:
click EXPAND for more on the Federal Papers, their purpose and authorship
- the essays were signed "Publius"
- Publius Valerius was one of founders of the Roman Republic who overthrew the Etruscan kings
Authors:
- Alexander Hamilton, John Jay and James Madison
click EXPAND for more on the authors
- Alexander Hamilton
- important federalist thinker and politician
- was Washington's first Secretary of the Treasury
- Hamilton applied federalist principles towards application of the central government's powers
- John Jay
- an important Revolutionary era patriot, diplomat and political leader
- Jay became the first Chief Justice of the U.S. Supreme Court
- James Madison
- provided the philosophical basis for the new Constitution
- became fourth president
- known as the "father of the Constitution" because:
- Madison set the agenda for the Constitutional Convention
- he created a "blueprint" (outline) for the new constitution
- and framed his ideas through history and philosophy
- Madison set the agenda for the Constitutional Convention
- Federalist Papers identified authorship:
- Alexander Hamilton (51 articles: Nos. 1, 6–9, 11–13, 15–17, 21–36, 59–61, and 65–85)
- John Jay (5 articles: Nos. 2–5 and 64).
- James Madison (29 articles: Nos. 10, 14, 18–20,[14] 37–58 and 62–63)
Publication
- the Papers were published in three New York newspapers
- Daily Journal, New-York Packet and Daily Advertiser
- they were reprinted elsewhere and subsequently printed as a collection
click EXPAND for more on publication of the Federalist Papers
"Addressed to the People of New York"
- New York State was a battleground for the arguments over adopting the proposed Constitution because of strong anti-federalist sentiment, including the Governor at the time, George Clinton.
- While the Federalist (so-called at the time) was reprinted elsewhere, it's largest circulation was in New York
- it is unclear the extent to which it influenced other states, such as Pennsylvania which ratified the Constitution amidst the publication of the Federalist Papers.
- Regardless of their direct impact upon the ratification of the Constitution, the Federalist Papers magnificently laid out the logic, reasons, and purposes of the proposed Constitution and have ever since been used by historians, the Courts, and the federal and state governments for guidance and clarification of the meaning of the Constitution.
Purpose of the Federalist Papers
- to explain and defend the proposed Constitution
- and to counter arguments made against it by the anti-federalists
- to influence the states to adopt the new constitution
Ideas behind the Papers
- to identify the need for a strong central government
- to identify the protections for the states and the people from that central government
- principally through separation of powers, checks & balances, and accountability to the people
Legacy of the Papers:
- stand as evidence of the ideas and intentions behind the design of the Constitution
- have been used in Courts in order to help define the legal meanings of the Constitution
- remind Americans of the philosophy of government behind the Constitution
Federalist No. 10 background[edit | edit source]
- Federalists 6-10 , in general, review the relationship between the states and with the proposed government
- especially the problem of "dissensions" (disagreement) between them
- In Federalist 10, Madison discusses the problem in a democracy of faction and how an extensive government with limited government can avoid it
- Federalist no. 6: Concerning Dangers from Dissensions Between the States (by Hamilton)
- Federalist no. 7: The Same Subject Continued: Concerning Dangers from Dissensions Between the States (by Hamilton)
- Federalist no. 8: The Consequences of Hostilities Between the States (by Hamilton)
- Federalist no 9: The Utility of the Union as a Safeguard Against Domestic Faction and Insurrection (by Hamilton)
- Federalist no. 10: The Same Subject Continued: The Union as a Safeguard Against Domestic Faction and Insurrection (by Madison)
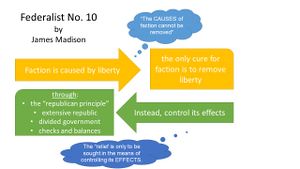
Federalist No. 10 Summary[edit | edit source]
- Madison discusses the inherent problem in self-government of "faction"
- he defines "faction" as any group that is opposed to another
- factions consist of people joining together for common purpose and common self-interest
- he identifies the problem with faction in that, if one faction seizes control of the government, it can use its powers to abuse the other factions or people
- Madison identifies the only means to avoid faction as removing liberty
- in other words, since faction is the result of groups using their liberties to seize power, the only way to stop it is to remove their liberties
- i.e., the cause of faction is liberty
- however, taking away liberties in order to remove faction is unacceptable
- therefore, Madison proposes, instead of removing the causes of faction, to mitigate (reduce or control) its effects
- Madison discussed the "republican principle" as:
- popular government through representative democracy
- separate branches
- checks & balances
- he points out that an "extensive" republic with divided and limited government will make it difficult for any one faction to seize complete control of it
- he contrasts that with the history of small republics and states that succumbing to faction and end up abusing the rights of citizens
- Madison's argument can also be seen as defense of limited government in a pluralistic, diverse society that is capable of self-rule and civil settlement of disputes
- key quotations:
- liberty is "essential to political life"
- "liberty is to faction what air is to fire"
- the solution to the problem of faction is "worse than the disease"
- "the CAUSES of faction cannot be removed... [so the ] relief is only to be sought in the means of controlling its EFFECTS."
| ORIGINAL TEXT | SUMMARY/ ANALYSIS |
|
FEDERALIST NO. 10
The Utility of the Union as a Safeguard Against Domestic Faction and Insurrection New York Packet, Friday, November 23, 1787 To the People of the State of New York: |
Authorship[edit | edit source]
Title[edit | edit source]
|
| AMONG the numerous advantages promised by a well-constructed Union, none deserves to be more accurately developed than its tendency to break and control the violence of faction. The friend of popular governments never finds himself so much alarmed for their character and fate, as when he contemplates their propensity to this dangerous vice. He will not fail, therefore, to set a due value on any plan which, without violating the principles to which he is attached, provides a proper cure for it. The instability, injustice, and confusion introduced into the public councils, have, in truth, been the mortal diseases under which popular governments have everywhere perished; as they continue to be the favorite and fruitful topics from which the adversaries to liberty derive their most specious declamations. The valuable improvements made by the American constitutions on the popular models, both ancient and modern, cannot certainly be too much admired; but it would be an unwarrantable partiality, to contend that they have as effectually obviated the danger on this side, as was wished and expected. Complaints are everywhere heard from our most considerate and virtuous citizens, equally the friends of public and private faith, and of public and personal liberty, that our governments are too unstable, that the public good is disregarded in the conflicts of rival parties, and that measures are too often decided, not according to the rules of justice and the rights of the minor party, but by the superior force of an interested and overbearing majority. However anxiously we may wish that these complaints had no foundation, the evidence, of known facts will not permit us to deny that they are in some degree true. It will be found, indeed, on a candid review of our situation, that some of the distresses under which we labor have been erroneously charged on the operation of our governments; but it will be found, at the same time, that other causes will not alone account for many of our heaviest misfortunes; and, particularly, for that prevailing and increasing distrust of public engagements, and alarm for private rights, which are echoed from one end of the continent to the other. These must be chiefly, if not wholly, effects of the unsteadiness and injustice with which a factious spirit has tainted our public administrations. |
Tendency of self-governments towards violence and faction[edit | edit source]
|
| By a faction, I understand a number of citizens, whether amounting to a majority or a minority of the whole, who are united and actuated by some common impulse of passion, or of interest, adversed to the rights of other citizens, or to the permanent and aggregate interests of the community. |
Faction defined[edit | edit source]
|
| There are two methods of curing the mischiefs of faction: the one, by removing its causes; the other, by controlling its effects. |
Mitigating effects of faction[edit | edit source]
|
| There are again two methods of removing the causes of faction: the one, by destroying the liberty which is essential to its existence; the other, by giving to every citizen the same opinions, the same passions, and the same interests. |
Removing faction[edit | edit source]
|
| It could never be more truly said than of the first remedy, that it was worse than the disease. Liberty is to faction what air is to fire, an aliment without which it instantly expires. But it could not be less folly to abolish liberty, which is essential to political life, because it nourishes faction, than it would be to wish the annihilation of air, which is essential to animal life, because it imparts to fire its destructive agency. |
"Liberty is to faction what air is to fire"[edit | edit source]
|
| The second expedient is as impracticable as the first would be unwise. As long as the reason of man continues fallible, and he is at liberty to exercise it, different opinions will be formed. As long as the connection subsists between his reason and his self-love, his opinions and his passions will have a reciprocal influence on each other; and the former will be objects to which the latter will attach themselves. The diversity in the faculties of men, from which the rights of property originate, is not less an insuperable obstacle to a uniformity of interests. The protection of these faculties is the first object of government. From the protection of different and unequal faculties of acquiring property, the possession of different degrees and kinds of property immediately results; and from the influence of these on the sentiments and views of the respective proprietors, ensues a division of the society into different interests and parties. |
Reason, passion & "diverse faculties of men"[edit | edit source]
|
| The latent causes of faction are thus sown in the nature of man; and we see them everywhere brought into different degrees of activity, according to the different circumstances of civil society. A zeal for different opinions concerning religion, concerning government, and many other points, as well of speculation as of practice; an attachment to different leaders ambitiously contending for pre-eminence and power; or to persons of other descriptions whose fortunes have been interesting to the human passions, have, in turn, divided mankind into parties, inflamed them with mutual animosity, and rendered them much more disposed to vex and oppress each other than to co-operate for their common good. So strong is this propensity of mankind to fall into mutual animosities, that where no substantial occasion presents itself, the most frivolous and fanciful distinctions have been sufficient to kindle their unfriendly passions and excite their most violent conflicts. But the most common and durable source of factions has been the various and unequal distribution of property. Those who hold and those who are without property have ever formed distinct interests in society. Those who are creditors, and those who are debtors, fall under a like discrimination. A landed interest, a manufacturing interest, a mercantile interest, a moneyed interest, with many lesser interests, grow up of necessity in civilized nations, and divide them into different classes, actuated by different sentiments and views. The regulation of these various and interfering interests forms the principal task of modern legislation, and involves the spirit of party and faction in the necessary and ordinary operations of the government. |
Faction is in the nature of man & its regulation is a role of government[edit | edit source]
|
| No man is allowed to be a judge in his own cause, because his interest would certainly bias his judgment, and, not improbably, corrupt his integrity. With equal, nay with greater reason, a body of men are unfit to be both judges and parties at the same time; yet what are many of the most important acts of legislation, but so many judicial determinations, not indeed concerning the rights of single persons, but concerning the rights of large bodies of citizens? And what are the different classes of legislators but advocates and parties to the causes which they determine? Is a law proposed concerning private debts? It is a question to which the creditors are parties on one side and the debtors on the other. Justice ought to hold the balance between them. Yet the parties are, and must be, themselves the judges; and the most numerous party, or, in other words, the most powerful faction must be expected to prevail. Shall domestic manufactures be encouraged, and in what degree, by restrictions on foreign manufactures? are questions which would be differently decided by the landed and the manufacturing classes, and probably by neither with a sole regard to justice and the public good. The apportionment of taxes on the various descriptions of property is an act which seems to require the most exact impartiality; yet there is, perhaps, no legislative act in which greater opportunity and temptation are given to a predominant party to trample on the rules of justice. Every shilling with which they overburden the inferior number, is a shilling saved to their own pockets. |
Power of the dominant faction in legislatures[edit | edit source]
|
| It is in vain to say that enlightened statesmen will be able to adjust these clashing interests, and render them all subservient to the public good. Enlightened statesmen will not always be at the helm. Nor, in many cases, can such an adjustment be made at all without taking into view indirect and remote considerations, which will rarely prevail over the immediate interest which one party may find in disregarding the rights of another or the good of the whole. |
Faction v. the public good[edit | edit source]
|
| The inference to which we are brought is, that the CAUSES of faction cannot be removed, and that relief is only to be sought in the means of controlling its EFFECTS. |
Faction cannot be stopped but its effects may be controlled[edit | edit source]
|
| If a faction consists of less than a majority, relief is supplied by the republican principle, which enables the majority to defeat its sinister views by regular vote. It may clog the administration, it may convulse the society; but it will be unable to execute and mask its violence under the forms of the Constitution. When a majority is included in a faction, the form of popular government, on the other hand, enables it to sacrifice to its ruling passion or interest both the public good and the rights of other citizens. To secure the public good and private rights against the danger of such a faction, and at the same time to preserve the spirit and the form of popular government, is then the great object to which our inquiries are directed. Let me add that it is the great desideratum by which this form of government can be rescued from the opprobrium under which it has so long labored, and be recommended to the esteem and adoption of mankind. |
Republicanism & faction[edit | edit source]
|
| By what means is this object attainable? Evidently by one of two only. Either the existence of the same passion or interest in a majority at the same time must be prevented, or the majority, having such coexistent passion or interest, must be rendered, by their number and local situation, unable to concert and carry into effect schemes of oppression. If the impulse and the opportunity be suffered to coincide, we well know that neither moral nor religious motives can be relied on as an adequate control. They are not found to be such on the injustice and violence of individuals, and lose their efficacy in proportion to the number combined together, that is, in proportion as their efficacy becomes needful. |
Two methods to control faction[edit | edit source]
|
| From this view of the subject it may be concluded that a pure democracy, by which I mean a society consisting of a small number of citizens, who assemble and administer the government in person, can admit of no cure for the mischiefs of faction. A common passion or interest will, in almost every case, be felt by a majority of the whole; a communication and concert result from the form of government itself; and there is nothing to check the inducements to sacrifice the weaker party or an obnoxious individual. Hence it is that such democracies have ever been spectacles of turbulence and contention; have ever been found incompatible with personal security or the rights of property; and have in general been as short in their lives as they have been violent in their deaths. Theoretic politicians, who have patronized this species of government, have erroneously supposed that by reducing mankind to a perfect equality in their political rights, they would, at the same time, be perfectly equalized and assimilated in their possessions, their opinions, and their passions. |
"Pure democracy" susceptible to faction[edit | edit source]
|
| A republic, by which I mean a government in which the scheme of representation takes place, opens a different prospect, and promises the cure for which we are seeking. Let us examine the points in which it varies from pure democracy, and we shall comprehend both the nature of the cure and the efficacy which it must derive from the Union. |
Republic defined[edit | edit source]
|
| The two great points of difference between a democracy and a republic are: first, the delegation of the government, in the latter, to a small number of citizens elected by the rest; secondly, the greater number of citizens, and greater sphere of country, over which the latter may be extended. |
Democracy v. republic: delegation & size[edit | edit source]
|
| The effect of the first difference is, on the one hand, to refine and enlarge the public views, by passing them through the medium of a chosen body of citizens, whose wisdom may best discern the true interest of their country, and whose patriotism and love of justice will be least likely to sacrifice it to temporary or partial considerations. Under such a regulation, it may well happen that the public voice, pronounced by the representatives of the people, will be more consonant to the public good than if pronounced by the people themselves, convened for the purpose. On the other hand, the effect may be inverted. Men of factious tempers, of local prejudices, or of sinister designs, may, by intrigue, by corruption, or by other means, first obtain the suffrages, and then betray the interests, of the people. The question resulting is, whether small or extensive republics are more favorable to the election of proper guardians of the public weal; and it is clearly decided in favor of the latter by two obvious considerations: |
Democracy v. republic analysis[edit | edit source]
|
| In the first place, it is to be remarked that, however small the republic may be, the representatives must be raised to a certain number, in order to guard against the cabals of a few; and that, however large it may be, they must be limited to a certain number, in order to guard against the confusion of a multitude. Hence, the number of representatives in the two cases not being in proportion to that of the two constituents, and being proportionally greater in the small republic, it follows that, if the proportion of fit characters be not less in the large than in the small republic, the former will present a greater option, and consequently a greater probability of a fit choice. |
Extensive republics: reason no. 1[edit | edit source]
|
| In the next place, as each representative will be chosen by a greater number of citizens in the large than in the small republic, it will be more difficult for unworthy candidates to practice with success the vicious arts by which elections are too often carried; and the suffrages of the people being more free, will be more likely to centre in men who possess the most attractive merit and the most diffusive and established characters. |
Extensive republics: reason no. 2[edit | edit source]
|
| It must be confessed that in this, as in most other cases, there is a mean, on both sides of which inconveniences will be found to lie. By enlarging too much the number of electors, you render the representatives too little acquainted with all their local circumstances and lesser interests; as by reducing it too much, you render him unduly attached to these, and too little fit to comprehend and pursue great and national objects. The federal Constitution forms a happy combination in this respect; the great and aggregate interests being referred to the national, the local and particular to the State legislatures. |
"The mean" -- how to balance representation[edit | edit source]
|
| The other point of difference is, the greater number of citizens and extent of territory which may be brought within the compass of republican than of democratic government; and it is this circumstance principally which renders factious combinations less to be dreaded in the former than in the latter. The smaller the society, the fewer probably will be the distinct parties and interests composing it; the fewer the distinct parties and interests, the more frequently will a majority be found of the same party; and the smaller the number of individuals composing a majority, and the smaller the compass within which they are placed, the more easily will they concert and execute their plans of oppression. Extend the sphere, and you take in a greater variety of parties and interests; you make it less probable that a majority of the whole will have a common motive to invade the rights of other citizens; or if such a common motive exists, it will be more difficult for all who feel it to discover their own strength, and to act in unison with each other. Besides other impediments, it may be remarked that, where there is a consciousness of unjust or dishonorable purposes, communication is always checked by distrust in proportion to the number whose concurrence is necessary. |
The large republic[edit | edit source]
|
| Hence, it clearly appears, that the same advantage which a republic has over a democracy, in controlling the effects of faction, is enjoyed by a large over a small republic,--is enjoyed by the Union over the States composing it. Does the advantage consist in the substitution of representatives whose enlightened views and virtuous sentiments render them superior to local prejudices and schemes of injustice? It will not be denied that the representation of the Union will be most likely to possess these requisite endowments. Does it consist in the greater security afforded by a greater variety of parties, against the event of any one party being able to outnumber and oppress the rest? In an equal degree does the increased variety of parties comprised within the Union, increase this security. Does it, in fine, consist in the greater obstacles opposed to the concert and accomplishment of the secret wishes of an unjust and interested majority? Here, again, the extent of the Union gives it the most palpable advantage. |
"The extent of the Union gives it the most palpable advantage"[edit | edit source]
|
| The influence of factious leaders may kindle a flame within their particular States, but will be unable to spread a general conflagration through the other States. A religious sect may degenerate into a political faction in a part of the Confederacy; but the variety of sects dispersed over the entire face of it must secure the national councils against any danger from that source. A rage for paper money, for an abolition of debts, for an equal division of property, or for any other improper or wicked project, will be less apt to pervade the whole body of the Union than a particular member of it; in the same proportion as such a malady is more likely to taint a particular county or district, than an entire State. |
Effects of faction will be isolated in a large republic[edit | edit source]
|
| In the extent and proper structure of the Union, therefore, we behold a republican remedy for the diseases most incident to republican government. And according to the degree of pleasure and pride we feel in being republicans, ought to be our zeal in cherishing the spirit and supporting the character of Federalists |
The extent and structure of the Union[edit | edit source]
|
|
PUBLIUS. |
All the Federalist papers were signed "Publius," a reference to a founder of the Roman republic |
Sources:
.