Cultural diffusion: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Cultural diffusion''' | '''Cultural diffusion''' | ||
[[File:Cultural_Diffusion.jpg|thumb|Process of cultural diffusion]] | [[File:Cultural_Diffusion.jpg|thumb|Process of cultural diffusion]] | ||
* the spread (diffusion) and mixing of people | * the spread (diffusion) and mixing of people | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
** culture, [[disease]], race, religion, identity, technology, etc. | ** culture, [[disease]], race, religion, identity, technology, etc. | ||
=== Cultural diffusion: movement, change & assimilation === | |||
* cultural diffusion causes change | * cultural diffusion causes change | ||
* cultural diffusion occurs when people of one place interact with another | * cultural diffusion occurs when people of one place interact with another | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
* bridges | * bridges | ||
* horses | * horses | ||
* mechanized transit, including | * mechanized transit, including | ||
** automobiles | |||
** railroads | ** railroads | ||
** steamboats | ** steamboats | ||
** telegraph / telephone | ** telegraph / telephone | ||
** radio / TV | * rails (pre-steam) | ||
** | * radio / TV | ||
* roads | |||
* writing | |||
* See also | * See also | ||
** [[Human Geography]] | ** [[Human Geography]] | ||
Revision as of 17:53, 11 June 2022
Cultural diffusion
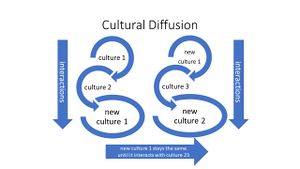
- the spread (diffusion) and mixing of people
- cultural diffusion operates through:
- trade, migration & warfare
- cultural diffusion spreads or mixes:
- culture, disease, race, religion, identity, technology, etc.
Cultural diffusion: movement, change & assimilation[edit | edit source]
- cultural diffusion causes change
- cultural diffusion occurs when people of one place interact with another
- in fact, people in any given "place" are the result of prior episodes (events, processes) of cultural diffusion
- the more movement in a region, the more that region
Geography & cultural diffusion[edit | edit source]
- isolation
- crossroads
- rivers as both "a highway and a moat"
- see geographic barriers: inhibitors to movement
- see geographic catalysts: facilitators to movement
- spreads more readily across similar climates and latitudes (east - west)
- rather than across different climates (north - south)
- spreads more readily across similar climates and latitudes (east - west)
Technology & cultural diffusion[edit | edit source]
- boats
- bridges
- horses
- mechanized transit, including
- automobiles
- railroads
- steamboats
- telegraph / telephone
- rails (pre-steam)
- radio / TV
- roads
- writing
- See also
Cultural diffusion as historical agent[edit | edit source]
- mixing of cultures, technologies, language, relgion, etc.
- Do the conquerors conquer the conquered or do the conquered conquer the conquerors?, examples:
- Mongol conquerors of China became Chinese (Yuan Empire)
- Turk invaders of Anatolia became Muslim
- Norman invaders of England became English
- Ptolemaic (Greek) rulers of Egypt