AP World History: Modern time line: Difference between revisions
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
| | | | ||
* Dar al-Islam, Pax Islamica | * Dar al-Islam, Pax Islamica | ||
* "caliph" = official Islamic religious and political ruler | |||
* by end of 9th century, was a fragmented empire with centrally-ruled and allied, autonomous rulers | * by end of 9th century, was a fragmented empire with centrally-ruled and allied, autonomous rulers | ||
* Baghdad remained the "ritualized court" for Sunni Islam in opposition to Shia Islam | * Baghdad remained the "ritualized court" for Sunni Islam in opposition to Shia Islam | ||
* subjected to Persian, Seljuk & other Turkic invasions | * subjected to Persian, Seljuk & other Turkic invasions | ||
* final collapse from Mongol invasion | * final collapse from Mongol invasion | ||
|[[File:Regions of the Lands of Islam by al-Muqaddasi.jpg|left|thumb|The lands and cities of the Dar al-Islam in the 10th century, according to the geographer al-Muqaddasi | |Click expand to view map Dar al-Islam in the 10th century (click on image to enlarge): | ||
<div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | |||
[[File:Regions of the Lands of Islam by al-Muqaddasi.jpg|left|thumb|The lands and cities of the Dar al-Islam in the 10th century, according to the geographer al-Muqaddasi]] | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
|960-1279 | |960-1279 | ||
| Line 68: | Line 72: | ||
* established Islamic capital at the ancient city, Dehli, India | * established Islamic capital at the ancient city, Dehli, India | ||
|South Asia | |South Asia | ||
| | |Persia, India | ||
|cultural diffusion | |cultural diffusion | ||
|Islam | |Islam | ||
| | | | ||
* Hindu hegemony over South Asia directly challenged by the Ghurid dynasty, which brought Islam to India | |||
* transferred Persian culture to northern India, including literature and architecture | * transferred Persian culture to northern India, including literature and architecture | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 88: | Line 94: | ||
|Islam | |Islam | ||
| | | | ||
* "sultan" = Arabic for "he who rules"; originally was not a hereditary title | |||
* established by a Ghurid general, a Turkish slave who became a military leader (a "'''Mamluk'''" = non-Arab slave given military and administrative duties) | * established by a Ghurid general, a Turkish slave who became a military leader (a "'''Mamluk'''" = non-Arab slave given military and administrative duties) | ||
* at peak controlled most of the subcontinent | * at peak controlled most of the subcontinent | ||
* 1526 = Mughal conquest | * weakened by Tamerlane (Mongol) invasion of 1398; he plundered Dehli and then left the subcontinent | ||
* Sultanate rule was further challenged by 14th century Hindu reconquests of southern India | |||
* 1526 = Mughal conquest ended the Sultanate, which by then was reduced to its original territorial rule in northern India | |||
| | | | ||
* | * | ||
| Line 102: | Line 111: | ||
|Genghis Khan | |Genghis Khan | ||
|Asia | |Asia | ||
| | |Mongols | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 121: | Line 130: | ||
|West Asia | |West Asia | ||
| | | | ||
| | |empire | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 137: | Line 146: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1260 | | 1260 | ||
|Mongol Empire divided into 4 khanates | |Mongol Empire divided into 4 khanates: | ||
| | * Yuan Dynasty (east Asia) | ||
| | * Golden Horde (northwest ) | ||
| | * Ilkhanate (southwest) | ||
* Chagatai (central) | |||
|Asia | |||
|Mongols | |||
|empire | |||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
* succession disputes arose among grandchildren of Genghis Khan over direction of Mongol rule as integrated into conquered areas or maintaining traditional steppe / nomadic identity | |||
* although Kublai Khan became emperor in 1260, he was nominal and not actual ("emperor in name only"). and each khanate was largely autonomous | |||
* | |||
|click expand for political map of Asia in 1335 showing Mongol Khanates before further disintegration of Mongol Empire | |||
<div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | |||
[[File:Asia in 1335.svg|left|thumb|Asia in 1335. Mongol states are Golden Horde, Ilkhanate, Chagatai Khanate & Yuan Dynasty]] | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| 1271-1295 | | 1271-1295 | ||
| Line 235: | Line 255: | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
|1336- | |1336-1572 | ||
|Vijayanagara Empire | |Vijayanagara Empire | ||
* Hindu empire in southern India | |||
* stopped Islamic spread to southern India by defeating the Deccan sultanates | |||
|South Asia | |||
|India | |India | ||
|cultural diffusion | |cultural diffusion | ||
|religion | |religion | ||
| | | | ||
* | * was slow to adopt cannon and other modern military technologies | ||
* | * fell to the sultanates when they combined and defeated the Vijayanagara army in 1565 | ||
* the capital was moved and the empire divided in 1572 | |||
| | | | ||
* Vijayanagara, the capital city, was famed for wealth and learning | * Vijayanagara, the capital city, was famed for wealth and learning | ||
| Line 278: | Line 302: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|1353 | |1353 | ||
|gunpower perfected in Germany | |gunpower perfected in Germany | ||
|Europe | |Europe | ||
|China | |China | ||
|technology | |technology | ||
|cultural diffusion | |cultural diffusion | ||
| | | | ||
* invented in 9th century in China, called "fire medicine" | * with improved metalworking, increased firing range and durability over early Chinese and Middle Eastern guns | ||
* Europeans acquired gunpowder via Silk Road exchange with the Mongol Empire | |||
* printing and paper technologies were also transmitted over the Silk Road | |||
| | |||
* gunpowder was invented in 9th century in China, called "fire medicine" | |||
* had limited use under Song Dynasty as "incendiary projectiles" but not adapted for common military use and not for cannon or guns | * had limited use under Song Dynasty as "incendiary projectiles" but not adapted for common military use and not for cannon or guns | ||
* Medieval Islam acquired recipes which included saltpeter, which they called "Chinese snow"; having already employed naptha (petroleum-based) as an incendiary | * Medieval Islam acquired recipes which included saltpeter, which they called "Chinese snow"; having already employed naptha (petroleum-based) as an incendiary | ||
* Mongol warfare included use of gunpowder, especially in conquest of China, and possibly in attacks on Europe, | * Mongol warfare included use of gunpowder, especially in conquest of China, and possibly in attacks on Europe, which may have been part of its introduction to Europe | ||
* see Gunpowder empires for Islamic empires that made extensive use of muskets and cannon | * see Gunpowder empires for Islamic empires that made extensive use of muskets and cannon | ||
* Europeans applied it to small arms and cannon, and it was instrumental in bringing an end to calvary supremacy of European knights (see the [https://school4schools.com/wiki/index.php?title=US_History_timeline_%26_concept_chart:_16th-18th_centuries_(to_1754)_British-American_colonies#Thirty_Years_War.2C_1618-1648 Thirty Years War]) | * Europeans applied it to small arms and cannon, and it was instrumental in bringing an end to calvary supremacy of European knights (see the [https://school4schools.com/wiki/index.php?title=US_History_timeline_%26_concept_chart:_16th-18th_centuries_(to_1754)_British-American_colonies#Thirty_Years_War.2C_1618-1648 Thirty Years War]) | ||
| Line 301: | Line 328: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |||
|1399-early 1400s | |||
|Timurid relations with Europe | |||
|Europe, West Asia | |||
|Mongols | |||
|globalism | |||
|cultural diffusion | |||
| | |||
* 1399-1400, Turco-Mongol emperor Tamerlane defeated the Ottomans in Syria | |||
* he sought alliances with European monarchs to oppose the Ottomans | |||
* each side exchanged diplomats, gifts and information | |||
| | |||
* was concurrent (same time as) to Ming dynasty overseas expeditions | |||
* similar to Franco-Mongol alliance of the early 13th century, which was designed to oppose Ottoman expansion | |||
|- | |- | ||
| 1405-1433 | | 1405-1433 | ||
| Line 378: | Line 419: | ||
!Main Ideas/ Notes | !Main Ideas/ Notes | ||
!Other | !Other | ||
|- | |||
|1450 | |||
|Fra Mauro map | |||
|Europe | |||
|World | |||
|exploration | |||
|globalism | |||
| | |||
* 1st European modern world map, created by Venetian monk, Niccolò de Conti in 1450 (took several years to make; he had traveled to ) | |||
* the map indicated a sea route between Europe and India around Africa | |||
* considered the first European map to be non-religious in nature or focus | |||
* it did not place Jerusalem at the longitudinal center, and it removed the Garden of Eden from the world map (which was traditionally located on the world map to the east) | |||
|Click expand to view map of the Fra Mauro Map (click on image to enlarge): | |||
<div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | |||
[[File:FraMauroDetailedMap.jpg|left|thumb|The Fra Mauro Map of the world. The map depicts Asia, Africa and Europe, with south to the top (standard for Muslim world maps). The map is considered highly accurate and the first modern map of the world, even though not correctly depicting all of Africa (or the PaciiAmericas)]] | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| 1453 | | 1453 | ||
| Line 392: | Line 449: | ||
* Islamic empires built / expanded on use of gunpowder, especially muskets and cannon | * Islamic empires built / expanded on use of gunpowder, especially muskets and cannon | ||
* Ottoman, Safavid, Mughal empires | * Ottoman, Safavid, Mughal empires | ||
* the Ottomans were the first to adopt the technology & used it most effectively | |||
|South Asia | |South Asia | ||
|West Asia | |West Asia | ||
| Line 400: | Line 458: | ||
* Gunpowder empires created stable economies and administrative states | * Gunpowder empires created stable economies and administrative states | ||
* engaged in cultural patronage (cosmopolitan) | * engaged in cultural patronage (cosmopolitan) | ||
|[[File:Islamic Gunpowder Empires.jpg|left|thumb|Islamic Gunpowder Empires]] | |Click expand to view map of the Gunpowder Empires (click on image to enlarge): | ||
<div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | |||
[[File:Islamic Gunpowder Empires.jpg|left|thumb|Islamic Gunpowder Empires]] | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| 1450s-1480s | | 1450s-1480s | ||
| Line 590: | Line 651: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1600 | | 1600 | ||
| | |English East India Company founded | ||
| | (later renamed "British East India Co.) | ||
| | |England | ||
| | |trade | ||
| | |colonialization | ||
|India | |||
| | | | ||
* formed for Indian Ocean trade | |||
* joint-stock company | |||
* seized control of the Indian subcontinent | |||
* had a private army 260,000 soldiers (double size of British army) | |||
* produced half of the word's trade revenue during the mid-1700s to early 1800s | |||
* Britain took over in 1858 and assumed direct control of India as a colony | |||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 663: | Line 731: | ||
|1674-1818 | |1674-1818 | ||
|Maratha Empire or Confederacy | |Maratha Empire or Confederacy | ||
* Hindu reconquest of the subcontinent | |||
|South Asia | |South Asia | ||
| | |religion | ||
|India | |India | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | * Hindu empire from the Western Deccan plateau | ||
* sought to establish "self-rule of Hindus" ("hindavi swaajya") | |||
* ended the Mughal Empire and ruled most of India until falling to the British East India Company | |||
|click Expand for maps of European colonization of Africa | |||
<div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | |||
[[File:Maratha Empire in 1758.png|left|thumb|Maratha Empire, as of 1760]] | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| 1687 | | 1687 | ||
| Line 677: | Line 753: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | |||
|- | |||
| 1689-1725 |1682-1725 | |||
|Peter the Great | |||
* westernized Russia on Enlightenment ideals and customs (imposed a "beard tax" to force Russians to shave; instituted the Julian calendar) | |||
* imposed compulsory education for nobles and built universities | |||
|Eurasia | |||
|Russia | |||
|cultural diffusion | |||
| | |||
| | |||
* reorganized medieval political structures to modern state, including to abolish the Duma (assembly of local lords) and replacing it with a senate | |||
* built new capital, St. Petersburg | |||
* built the Imperial Navy | |||
* warred with Swedes for control of the Baltic Sea, the Ottomans for control of the Black Sea, and the Safavids (Persian) for control of the Caspian Sea | |||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 687: | Line 779: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1689 | | 1689 | ||
| Line 917: | Line 1,007: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| | |globalism | ||
| | |colonialism | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 978: | Line 1,068: | ||
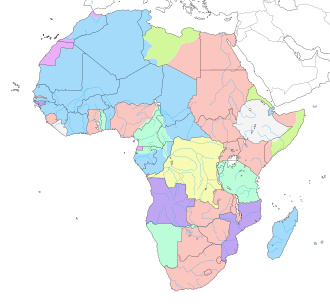
| 1885 | | 1885 | ||
|Berlin Conference & the "scramble for Africa | |Berlin Conference & the "scramble for Africa | ||
|Africa | |||
|Europe | |||
|colonization | |||
|globalism | |||
| | | | ||
| | * called "New Imperialism", 1881-1914 | ||
| | * the only African countries to avoid colonization during this time were Liberia & Ethiopia | ||
| | * by 1870, most European holdings in Africa were coastal (occupying 10% of land) | ||
| | * industrialization and transportation advances incentivized European search for raw materials and new markets | ||
* primary British motive was control of ports for trade with India | |||
|click Expand for maps of European colonization of Africa | |||
<div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | |||
[[File:Colonial Africa 1913 map.svg|left|thumb|Areas of Africa controlled by European colonial powers in 1913 (Belgian (yellow), British (red), French (blue), German (turquoise), Italian (green), Portuguese (purple), and Spanish (pink) Empires). Only Liberia and Ethiopia remainded independent (white)]] | |||
[[File:Scramble-for-Africa-1880-1913-v2.png|left|thumb| European colonization of Africa, 1880 and 1913 comparison]] | |||
</div> | |||
|- | |- | ||
| 1890s | | 1890s | ||
| Line 1,055: | Line 1,154: | ||
| 1904 | | 1904 | ||
| U.S. starts Panama Canal | | U.S. starts Panama Canal | ||
|Americas | |||
|Panama | |||
|globalism | |||
|colonialism | |||
| | | | ||
* a French attempt to build a canal across the Isthmus failed | |||
* US assisted a Panamanian revolt against Columbia by sending a warship to the harbor | |||
* the new government granted the US rights to build the canal | |||
* completed in 1914 | |||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 1,177: | Line 1,280: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
* hyper-inflation in Germany | |||
* Great Depression, New Deal in US (1933-39) | |||
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1931 | | 1931 | ||
|Japanese invasion of Manchuria | |Japanese invasion of Manchuria | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
Latest revision as of 13:00, 14 May 2022
AP World History: Modern timeline, 1200-present
Article purpose:
- timeline via sortable chart columns
- associate time, place, theme and make connections
Units 1-2, 1200 to 1450[edit | edit source]
| Dates | Place/Empire | Region | Place | Theme 1 | Theme 2 | Main Ideas/ Notes | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 750-1258 | Abbasid Caliphate
|
West Asia & North Africa | MidEast | religion | Islam |
|
Click expand to view map Dar al-Islam in the 10th century (click on image to enlarge): |
| 960-1279 | Song Dynasty | China | |||||
| 1095-1492 | Crusades | Europe | religion | ||||
| 1173-1206 | Ghurid dynasty
|
South Asia | Persia, India | cultural diffusion | Islam |
|
|
| 1206-1526 | Delhi Sultanate
|
South Asia | cultural diffusion | Islam |
|
| |
| 1206-1277 | Genghis Khan | Asia | Mongols | ||||
| 1215 | Magna Carta | Europe | England | ||||
| 1258 | Abbasid Caliphate ends | West Asia | empire |
|
|||
| 1271-1285 | Mongol invasion of Japan fails | ||||||
| 1260 | Mongol Empire divided into 4 khanates:
|
Asia | Mongols | empire |
|
click expand for political map of Asia in 1335 showing Mongol Khanates before further disintegration of Mongol Empire | |
| 1271-1295 | Marco Polo's travels | ||||||
| 1260-1350 | Pax Mongolia | ||||||
| 1279 | peak of Mongol Empire | ||||||
| 1279-1368 | Yuan Dynasty in China (Mongol rule) | ||||||
| 1282 | introduction of water-powered paper-mill " | China | technology | ||||
| 1299-1923 | Ottoman Empire | ||||||
| 1400-1600 | Italian Renaissance | ||||||
| 1324 | Mansa Musa pilgrimage to Mecca | ||||||
| 1325 | Tenochitlan founded | ||||||
| 1325-1354 | Ibn Battuta's travels | ||||||
| 1336-1572 | Vijayanagara Empire
|
South Asia | India | cultural diffusion | religion |
|
|
| 1346 | Black Death in China | ||||||
| 1347-1388 | Black Death in Europe | ||||||
| 1351-1368 | Red Turban Rebellion | ||||||
| 1353 | gunpower perfected in Germany | Europe | China | technology | cultural diffusion |
|
|
| 1368-1644 | Ming Dynasty | ||||||
| 1399-early 1400s | Timurid relations with Europe | Europe, West Asia | Mongols | globalism | cultural diffusion |
|
|
| 1405-1433 | Zheng He's treasure voyages | ||||||
| 1428-1521 | Aztec Empire | ||||||
| 1438-1533 | Inca Empire | ||||||
| 1440 | Swahili city-states | ||||||
| 1440 | Guteneberg invents printing press | ||||||
| 1400s | Portuguese caravel developed | ||||||
| 1441 | Atlantic slave trade in Atlantic islands |
Units 3-4, 1450-1750[edit | edit source]
| Dates | Place/Empire | Region | Place | Theme 1 | Theme 2 | Main Ideas/ Notes | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1450 | Fra Mauro map | Europe | World | exploration | globalism |
|
Click expand to view map of the Fra Mauro Map (click on image to enlarge): |
| 1453 | Ottoman conquest of Constantinople & collapse of Byzantine empire | Europe | empire | ||||
| 1453-1736 | Gunpowder empires
|
South Asia | West Asia | technology | economy |
|
Click expand to view map of the Gunpowder Empires (click on image to enlarge): |
| 1450s-1480s | Russia overthrows Mongol rule in Moscow | ||||||
| 1464-1591 | Songhai Empire | ||||||
| 1469 | Sikhism begins | ||||||
| 1492 | Reconquista of Spain completed | ||||||
| 1492 | Columbus's 1st voyage to Americas | ||||||
| 1498 | Vasco da Gama reaches India | ||||||
| 1501-1722 | Safavid Empire | ||||||
| 1534 | African slaves trade to Americas starts | ||||||
| 1509-1543 | Nzinga Mbemba (Afonso I) rules Kongo Empire | ||||||
| 1517 | Martin Luther's 95 Theses | ||||||
| 1519-1521 | Magellan voyage around the world | ||||||
| 1526-1748 | Mughal Empire
|
South Asia | India | religion |
|
||
| 1534 | France claims St. Lawrence riverway (Quebec colony) | ||||||
| 1543 | Copernicus / heliocentric universe | ||||||
| 1545 | Potosi mine opened in Bolivia | ||||||
| 1550-1700 | Scientific Revolution | ||||||
| 1552 | Russian Empire begins | ||||||
| 1556-1605 | Akbar the Great of the Mughal Empire | ||||||
| 1571 | Manila founded by Spanish | ||||||
| 1595 | Dutch "Fluyt" cargo ship introduced | ||||||
| 1600 | English East India Company founded
(later renamed "British East India Co.) |
England | trade | colonialization | India |
|
|
| 1600-1826 | Tokugawa shogunate | ||||||
| 1602 | Dutch East India Company founded | ||||||
| 1607 | Britain begins colonizing the Americas with Jamestown | ||||||
| 1623-1641 | Tokugawa Iemitsu rules Japan | ||||||
| 1632 | Taj Mahal built | ||||||
| 1643-1715 | Louis XIV rules France | ||||||
| 1652 | Boers colonize South Africa | ||||||
| 1674-1818 | Maratha Empire or Confederacy
|
South Asia | religion | India |
|
click Expand for maps of European colonization of Africa | |
| 1687 | Newton publishes Principia | ||||||
| 1682-1725 | Peter the Great
|
Eurasia | Russia | cultural diffusion |
|
||
| 1688-1911/12 | Qing (Manchu) Empire | ||||||
| 1689 | Glorious Revolution in England | ||||||
| 1698 | Early steam engine invented | ||||||
| The Enlightenment |
Units 5-6, 1750 to 1900[edit | edit source]
Units 7-9, 1900 to Present[edit | edit source]
| Dates | Place/Empire | Region | Place | Theme 1 | Theme 2 | Main Ideas/ Notes | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1904 | U.S. starts Panama Canal | Americas | Panama | globalism | colonialism |
|
|
| 1904-1905 | Russo-Japanese War | ||||||
| 1906 | Muslim League founded | ||||||
| 1910-1920 | Mexican Revolution | ||||||
| 1914-1918 | World War I | ||||||
| 1915-1917 | Armenian genocide | ||||||
| 1917 | Russian revolution | ||||||
| 1917 | Zimmerman telegram & US entry to WWI | ||||||
| 1920 | League of Nations established | ||||||
| 1922 | Stalin assumes Soviet leadership | ||||||
| 1922 | Ottoman empire ends | ||||||
| 1923 | Turkey established | ||||||
| 1927-1936 | Chinese Civil War | ||||||
| 1929-1939 | worldwide economic depressions |
|
|||||
| 1931 | Japanese invasion of Manchuria | ||||||
| 1936-1938 | Great Purge in USSR | ||||||
| 1939-1945 | World War II | ||||||
| 1941 | Pearl Harbor attack | ||||||
| 1941-1945 | Holocaust | ||||||
| 1941-1953 | Stalin total rule | ||||||
| 1943-1949 | Greek civil war | ||||||
| 1943-1978 | Green Revolution | ||||||
| 1945-1950 | Chinese Communist Revolution | ||||||
| 1945 | atomic bombs dropped | ||||||
| 1946 | Philippine independence | ||||||
| 1947 | Partition of India | ||||||
| 1947 | Japanese Empire formally ended | ||||||
| 1947 | Truman Doctrine | ||||||
| 1947-1990 | Cold War | ||||||
| 1948 | Israel founded | ||||||
| 1949 | NATO established | ||||||
| 1950-1953 | Korean War | ||||||
| 1953-1959 | Cuban Revolution | ||||||
| 1955 | Warsaw Pact founded | ||||||
| 1955 | Bandung Conference | ||||||
| 1955 | Polio vaccine introduced | ||||||
| 1955-1975 | Vietnam War | ||||||
| 1956 | Khrushchev takes power | ||||||
| 1958-1962 | Great Leap Forward/ Cultural Revolution | ||||||
| 1960 | "Year of Africa" | ||||||
| 1961 | President Eisenhower warns of "military-industrial complex" | ||||||
| 1962 | Cuban Missile Crisis | ||||||
| 1966-1976 | Cultural Revolution | ||||||
| 1973-1990 | Pinochet coup | ||||||
| 1977-1989 | Deng Xiaoping assumes power | ||||||
| 1979 | Iranian Revolution | ||||||
| 1989 | Tiananmen Square protests | ||||||
| 1989 | fall of the Berlin Wall | ||||||
| 1990 | collapse of USSR | ||||||
| 1990 | Apartheid ended | ||||||
| 1991 | Gulf War | ||||||
| 1994 | Rwandan genocide | ||||||
| 2001 | Sept 11 attacks | ||||||
| 2003+ | War on Terrorism | ||||||
| 2011 | Arab Spring |