|
1763 Treaty of Paris
- settled the French-Indian War, expanding British holdings in North America
1783 Treaty of Paris
- ended American Revolution
1791 Vermont Republic
- Vermont was an independent republic 1777-1791
1802 Louisiana Purchase
- from Mississippi River to the north & west, those borders undefined
1815 Treaty of Ghent
1818 Treaty of 1818
- created 49th parallel agreement
1819 Adams-Onis Treaty
- acquisition of Florida from Spain
1842 Webster–Ashburton Treaty
1845 Texas annexation
- Republic of Texas entered Union
1846 Oregon Treaty
- Britain recognized US ownership of "Oregon Lands"
1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
- settled Mexican-American War, "Mexican cession" of modern Southwest US, UT, NV & CA
1853 Gadsden Purchase
- US acquired additional lands south of NM and AZ from Mexico
1867 Alaska Purchase
1898 Treaty of Paris
- settled Spanish-American War (Puerto Rico & Philippines)
1898 Annexation of Hawaii
- the Newlands Resolution annexed the Republic of Hawaii
|
BIG IDEAS
What does it MEAN?
- Understanding American history and experience through territorial expansion
- motives, outcomes
- conflicts, impact
- land claims, economic opportunities
Push & pull factors
- land ownership & use
- economic opportunity
- business expansion, especially railroads
- gold & silver rushes
- trade, especially in Pacific Ocean expansion
Colonial expansion
- English settlers pushing westward from coastal settlements
- created conflict with Native Americans
- created conflict between Native Americans tribes and confederations
- created conflict with French and its fur trade with Native Americans
- led directly to French-Indian War
- Proclamation of 1763 forbade American colonists from settling west of the Appalachians
- = British attempt to control colonials westward push
- Spanish/French settlement in current US areas was limited
- their colonial impulse was for trade (French) and religious conversion of Native Americans (Spanish)
- English colonials sought settlement and populations grew rapidly
Exploration, fur trade, land
- Daniel Boone (1734-1820) and trailblazers, frontiersmen
- frontier culture and folk heroes
Northwest Ordinance of 1787
- the new nation recognized need to organize territorial expansion
- drove further claims westward
Manifest Destiny
- Republic of Texas declared after
- westward extension of railroads drove western settlement
- resulted in political disagreement/ sectionalism over expansion of free and slave territories and states
- Mexican-American War of 1846
- California Gold Rush of 1849
Civil War impact
- Transcontinental railroad
- Homestead Act of 1862
- Homesteaders and pioneers
- "land grants" of up to 160 acres
Impact of technologies
- steam power
- first used on boats in late 17th century
- railroads (starting 1820s)
- telegraph (1830s) & telephone (1870s)
- electricity
- automobiles & airplanes (starting early 20th century)
- American commercial and technological dominance (transistor, space race, etc.)
Overseas expansion & acquisitions
- transoceanic trade
- especially with introduction of steam boats
- = created need for coaling stations for refueling across Pacific Ocean
- Panama Canal as outgrowth of Spanish-American War
- industrialization
Expansion via acquisition from European powers
- Eastern Louisiana Territory, Ohio Valley & Northwest Territory from Britain
- Louisiana Territory and Florida acquisitions
- Mexican-American War
- Spanish-American War
Expansion via acquisition or war with Native Americans
Twentieth Century US overseas interventions
- foreign loans and direct investment (1910s Gunboat diplomacy & later 20th century US business dominance)
- petroleum & mining investments
- WWII
- US bases around world following the War
- American commercial & cultural dominance
- IBM, GM, Ford
- Hollywood & music industry (popular culture)
- internet, Microsoft, Google
|
 Map of the United States and territories after the Treaty of Paris=== British colonial expansion === Map of the United States and territories after the Treaty of Paris=== British colonial expansion ===
- 1667 Treaty of Breda
- Netherlands ceded "New Netherland" which the British renamed "New York"
- Within New Netherland, the Dutch (Netherlands) had claimed coastal areas of modern RI, CT, NY, NJ and DE
- 1715 Peace of Utrecht
- settled European conflict
- Britain seized control of the Asiento de Negros Spanish grants of right to engage in the African slave trade
- France ceded Newfoundland (eastern coast of Canada) to the British
- 1763 Treaty of Paris
- settled the French-Indian War
- Britain took all French territories in modern Canada
- France also ceded the eastern portion of the Louisiana Territory, which included lands from the Appalachian Mountains to the Mississippi River
- Spain ceded "Eastern Florida" (the "Panhandle" region)
US territorial expansion
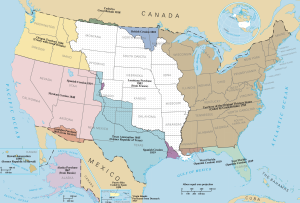 UnitedStatesExpansion UnitedStatesExpansion
- 1777 Vermont Republic
- 1783 Treaty of Paris
- Britain ceded the original 13 colonies and corresponding territories west to the Mississippi River
- the cessation included the Northwestern Territory, including the Ohio Valley, and the upper-midwest below the Great Lakes
- 1791 Vermont Republic
- Vermont had declared itself an independent state in 1777
- was admitted to the Union in 1791
- the admission settled claims by New York on Vermont lands
- 1818 Treaty of 1818
- Britain ceded land northwest of the Northwest Territory (western modern MN and north & east ND)
- US ceded lands north of the 49th parallel above modern MT
- established the 49th parallel as the border of US and Canada from MN to the Rocky Mountains (leaving Oregon Country in joint-control)
- called for "joint occupation" by British and Americans of Oregon Country (northwest corner of present US, including OR, WA, ID)
- 1819 Adams-Onis Treaty
- Spain ceded Florida to the US
- 1842 Webster–Ashburton Treaty
- settled border disputes along modern US-Canadian border, including in the modern states of ME, MN, MT, ID & WA (reaffirming the 49th parallel)
- 1846 Oregon Treaty
- Britain ceded claims to "Oregon Country," setting the 49th parallel across to the Pacific Ocean as the northern border
- Oregon Country included modern OR, WA, ID and parts of WY and MT
- 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
- settled Mexican-American War
- "Mexican cession" of southwestern territory, called "Alta California
- included modern NM, AZ, UT, NV and CA and parts of modern CO and TX
- 1853 Gadsden Purchase
- negotiated after the Mexican-American war to purchase Mexican territory in the south of modern AZ and southwest area of NM
- includes modern AZ cities of Yuma & Tucson
- cost was $10 million and motive for Mexico to sell it was likely to get the money before the Americans fully populated and/or seized it
- US was motivated by railroad route through the region
 Census Bureau map depicting territorial acquisitions and dates of statehood, probably created in the 1970s Census Bureau map depicting territorial acquisitions and dates of statehood, probably created in the 1970s
- 1867 Alaska Purchase from Russia for $7.2 million
- Russian motives:
- Russia had originally exploited the region for its fur trade and never populated it
- by 1850s sea otters were hunted to near extinction
- the Russians understood Alaska would be difficult to defend against US or British attack
- they preferred to sell it to the US as a buffer against the British
- US opponents called it "Seward's Folly" after Secretary of State Seward who negotiated the purchase
- US proponents thought it would help promote trade with Asia
- Alaska's extensive mineral deposits were not yet discovered (starting with Klondike Gold Rush in 1896)
- Alaska became a state in 1948
- 1898 Treaty of Paris
- settled Spanish-American War
- Spain recognized an independent Cuba and ceded Puerto Rico, Philippines and Guam to the US
- US compensated Spain for the cessations $20 million
- US set up Cuba as an independent country
- US kept Puerto Rico, Philippines and Guam (as part of the Marianas Islands) as territories
- Puerto Ricans were granted US citizenship in 1917
- Philippines:
- Philippine-American War, or "Tagalog Insurgency" ensued from 1986-1902
- Philippine nationalists sought full independence
- pockets of resistance continued until 1913
- Philippines remained an American territory until 1946
- 1898 Annexation of Hawaii
- throughout the 1800s, Americans settled in Hawaii for sugar planting and trade
- the Republic of Hawaii was created by white Americans in 1984 after overthrowing the indigenous Hawaiian Kingdom
- the Newlands Resolution annexed the Republic of Hawaii
- the Territory of Hawaii was established in 1900
- Hawaii became the 50th state in 1959
Acquisition or takeover of Native American lands
- Northwestern Territory
- Georgia
- Oklahoma
- Dakotas
Pacific Island and other acquisitions
- 1856 Guano Islands Act
- Congress declared that US citizens could take possession of any unclaimed "guano" islands and would receive US government protection
- were islands that held "guano" deposits (used as fertilizer and saltpeter, an ingredient in gunpowder)
- about 100 claims were made in Atlantic, Caribbean and Pacific waters
- 1867 Midway Atoll
- originally claimed under the Guano Islands Act, Midway islands were officially annexed by the US in 1867
- Midway served as important US Naval base
- 1903 Panama Canal Zone
- US seized the "Canal Zone" from Columbia in 1903 by supporting Panamanian independence from Columbia with support of US warships
- the Canal Zone was receded to Panama in 1999
|


