Religion
Religion
Origins & cultural practice
Explaining the world
World and human origins
- Humans naturally want to know "why"
- Why are we here?
- religions and founding myths usually intersect
- What is our purpose?
- religions
Purpose of life
- a primary function of religion is to order daily life
- religion may guide
- social structures
- political structures
- class, profession, and other hierarchies
- note that the word "hierarchy" originally means "rank in the sacred order" (see heirarchy word origin (etymonline)
Reflect or reinforce social structures
- religious belief provides authenticity and legitimacy to political, social and cultural systems or structures
- ex.:
- across human history, hereditary rule (especially monarchy) is the most stable political system
- because the "first born" of the ruler is selected by God/gods
- therefore the first born is legitimized by belief in that God/gods
- because the "first born" of the ruler is selected by God/gods
- across human history, hereditary rule (especially monarchy) is the most stable political system
Mitigating Uncertainty
Ritual
- burial
- sacrifice
- purpose
- types of sacrifice
- animal sacrifice
- human sacrifice
Superstition
- 13 and Friday the 13th superstitions
- many ancient counting systems, especially Babylonian, were 12-base
- therefore 13 marked a bad number
- in Christianity, Judas was considered the 13th disciple at the Last Supper
- since he betrayed Jesus, 13 is associated with him
- it is likely that the prejudice against pre-existed the story of the Last Supper and Judas
- many ancient counting systems, especially Babylonian, were 12-base
- see:
Prehistoric
- animism
- polytheism
Paleolithic
- conceptual thought
- spirituality
- examples
- cave paintings
- pictograms
- figurines
- Venus figurine
- lion man
- totemism
Neolithic
- examples
- ritual burial
- megaliths
Ancestor Worship
- Neolithic origins *
Mythology
Polytheism
Organized Religions
- listed in approximate chronological order of development
Hinduism
Zoroasterism
Bhuddism
Abrahamic religions
Judaism
- Old Testament
Christianity
- New Testament
Islam
Worldwide religiosity
Pew Research 2018 worldwide survey
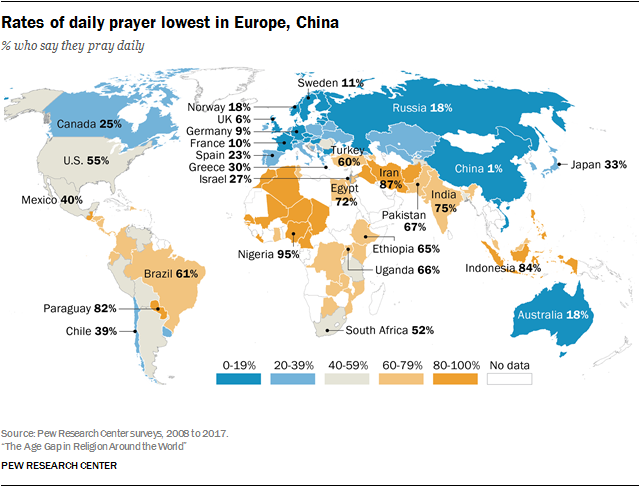
Worldwide rates of daily prayer rates
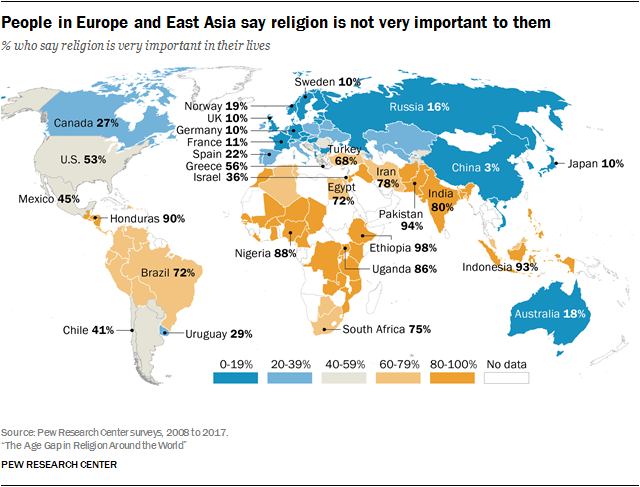
Worldwide importance of religion rates
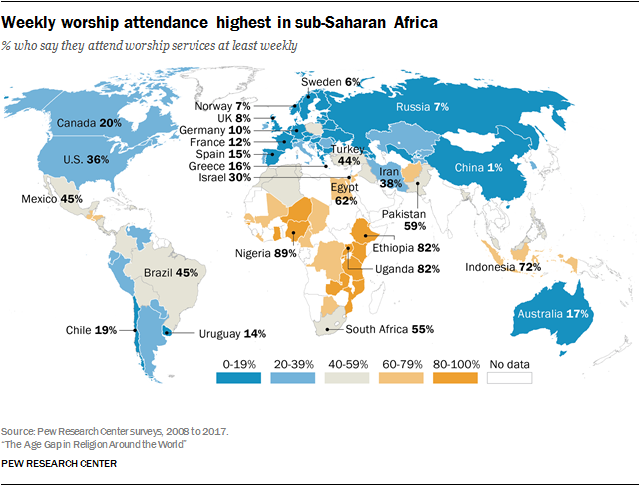
Worldwide weekly religious attendance rates
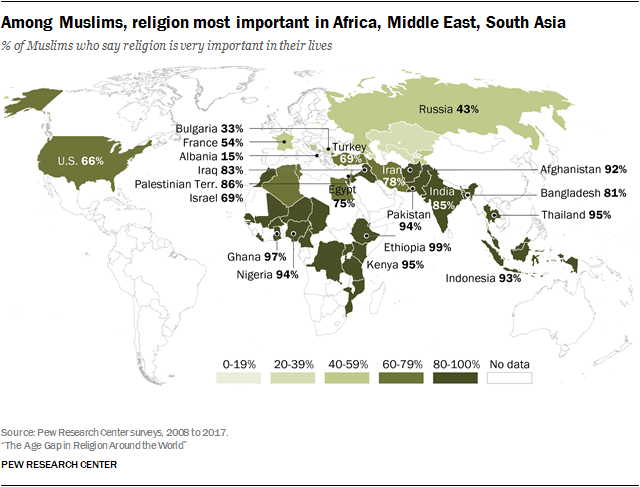
Worldwide religion importance rates
Teaching religion
Curricular objectives
- non-judgmental, facts-based learning
- i.e., "this religion"
- exists in...
- believes in...
- practices...
- i.e., "this religion"
Religion pedagogy & teaching strategies
- maintain objectivity
- promote respect
- never violate or directly challenge a student's own religious views
- Example of religious teaching: Catholic Catechism (rejoiceinmary.org)