Turning points
Turning Points (or Paradigm Shifts)
Objectives:
- to evaluate change and its causes and effects
- to comprehend and compare time, change, and causality
- to evaluate why change does not occur (stability v. change)
- to comprehend that different things take place at different places and times across history (Contingency)
Note:
- this page can be used alternatively with timelines, or be used to generate timelines
Major Turning Points in World History
Prehistory
Paleolithic Age
- Early Hominids
- fire
- tools
- domestication of dogs
- Cro-Magnum man:
- >> link to early modern humans page
[Ice Age]
- settlement of the Americas
{End of Ice Age] (Holocene Era)
- Natufian society
- settlement
- rise of the oceans
Neolithic Age
- semi-permanent or permanent settlement
- domestication of plants
- domestication of herd animals
Rise of Civilization
- metal working
- Copper Age
- Bronze Age
- domestication of horses for transportation
- domestication of camels for transportation
- rise of cities and complex social structures
Civilization
writing
- oral traditions made permanent with writing
- written law (Hammuarabi's Code)
technologies
- Iron Age
- mass
- astronomy & mathematics
- navigation
- architecture
- warfare
empires
- Akkadian empire (first empire)
- Qin Dynasty
- Persian empire
- Roman empire
Classical period
- Hellenistic Age
- Athens
- Rome
key events and years 4000 BC to 1 AD
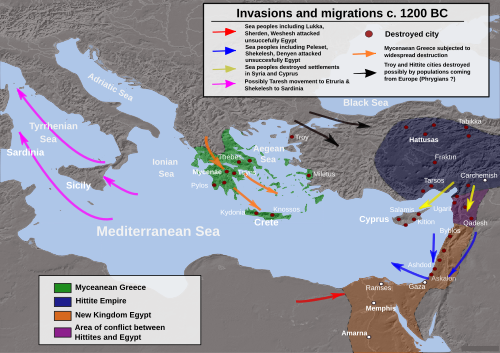
1177 BC
- Bronze Age Collapse
1 AD
- birth of Christ
key events and years 1 AD to modern period
313
- Edict of Milan: officially tolerates Christians across Roman Empire
325
- Constantine the Great unifies Roman empire
476
- Collapse of western Roman empire
632 Mohammad dies
732
- Battle of Tours
1206
- Genghis Kahn arises
1215
- Magna Carta
1453
- Fall of Byzantium to Ottomans
1455
- Gutenberg invents moveable type press
1487
- Aztec completion of the Sixth Temple at the Templo Mayor in Tenochtitlan
- the population of Tenochtitlan was between 200,000-400,000 (see Tenochtitlan)
1488
- Portuguese reach Indian Ocean via Africa Bartolomeu Dias
1492
- Columbus discover of America
- other
- Machiavelli
1517
- Luther's 95 Theses
- sparks Protestant Reformation
1588 English defeat of Spanish Armada
- rise of Britain
- decline of Spain
1648
- Treat of Westphalia ends 30 Years War
- ruinous political and religious war ends w/ independent German states able to choose religion (protestant v. Catholic)
1688
- British Glorious Revolution
- ended British divine rule and affirmed Parliament's power
1740
- Federick the Great of Prussia
- Catherine the Great of Russia
- balance of power shifts away from Austria
1776
- Declaration of Independence, July 4, 1776
1789
- US Constitution affirmed and election / inauguration of Washington as 1st president
- French Revolution
1815
- Congress of Vienna restores monarchies after fall of Napoleon
1848
- popular & radical revolts in Europe fail
1870
- unification of Germany
1914-18 WWI
1917
- Russian communist revolution
1929
- Stock Market crash
1930s
- Great Depression
- rise of Hitler and the German National Socialist Party (Nazi)
1939-45
- WWII
1989
- collapse of Soviet Union
Modern technologies
- Franklin Stove
- lightning rod
- Thomas Crapper
- electricity
- automobile
- medicine
- modern Air Conditioner 1902 by Willis Carrier
- first home air conditioner, 1914
- installation of air conditioners in motive theaters: 1925
- common use of air conditioners in homes: 1950s
- sources:
See also
- Ages of Man - the ancient Greek mythological stages of mankind (Golden Age, Silver Age, Bronze Age, Heroic Age, Iron Age)