Geography vocabulary
Geography Vocabulary [category:Geography] [category:Social Studies] [category:Social Studies Skills]
- code for EXPAND/COLLAPSE functions:
code: <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:50%"> text * for bullets * '''>''' for bullets with bold </div> * Click EXPAND to see list of important >>
Five Themes of Geography
- Location
- Absolute Location
- Relative Location
- Regions
- Place
- Movement
- Human-Environment Interaction (Relationships within Places)
- Cultural Diffusion
- See Social Studies Skills
Map terminology
- Latitude
- Longitude
- Equator
- Prime Meridian
- International Dateline
- Meridians
- Parallels
- a.m. / p.m.
- equinox
- solstice
- Tropic of Cancer
- Tropic of Capricorn
Physical Geography
- the study of the elements that constitute the earth's surface and how they interact
- includes meteorology, which is the study of weather and weather prediction
- [Physical geography(wiki)]
Water bodies
bay
canal
- man-made straits that connect two larger bodies of water
- canals provide important water passage to connect water bodies that would otherwise require long-distance water travel around land bodies or continents
- usually canals are built across isthmuses
- Bahr Yussef
- connects the Nile to the Faiyum Oasis and Lake Moeris, built 2300 BC
- Canal of the Pharaohs
- connected the Nile to the Red Sea
- built by Necho II, Assyrian ruler of Egypt in 7th century BC
- Persian king Darius I bragged of building a canal linking the Nile to the Red Sea (6th century BC)
- Corinth Canal
- Grand Canal
- connected the Yellow and Yangtze Rivers, built under the Sui dynasty (6th century AD)
- Suez Canal
- Panama Canal
- Click EXPAND to see list of important canals
channel
- synonymous with "strait" but usually referring to a smaller or less important strait
- see strait below
delta
gulf
lake
ocean
sea
- to do
- epicontinental sea
- = sea levels above continental shelfs, thus 400 ft or above sea level
strait
- a narrow body of water that connects larger bodies of water, or, a narrow channel that separates land masses
- synonymous with channel, passage, or pass
- implicit in the terminology is that the strait allows for navigation, or passage, from one larger body of water to another
- "strait comes from Old French "estreit" for "tight" or "narrow"
click EXPAND to see list of important straits:
- important straits and channels
- Bosporus Strait
- connects Black Sea to Aegean/Mediterranean Seas
- Strait of Gibraltar
- connects Mediterranean Sea to Atlantic Ocean
- ancient Greeks called the promontories on either side of the Strait of Gibraltar the "Pillars of Hercules", which marked the passage from the Mediterranean Sea into the Atlantic Ocean
- Strait of Magellan
- connects Atlantic and Pacific Oceans
- the passageway near the southern tip of South America that was navigated by the explorer Ferdinand Magellan, who led the first expedition to circumnavigated the globe
- the Strait of Magellan is not "straight" -- is actually a U-shaped pathway formed by the Tierra del Fuego archipelago (chain of islands)
- Beagle Channel
- a second, less navigable passageway near the southern tip of South America that was navigated by Charles Darwin on the HMS Beagle
- NOTE: the open-ocean passageway, around the very tip of South America is called "Drake's Passage", named for English explorer Francis Drake who circumnavigated the globe
- Strait of Hormuz
- Bass Strait
- between Australia and Tasmania
- Bering Strait
- Strait of Messina
- Bab-el Mendeb Strait
- Strait of Malacca
- Strait of Dover
- Strait of Singapore
- See:
river
- rivers flow downhill, usually but not always into an ocean
- upstream v. downstream
- tributary
- estuary
- Gulf of Ob
- world's longest estuary
- fed by the Ob River and feeding into the Kara Sea (part of the Arctic Ocean)
- delta
- silt
- flow & discharge
- measurement of the amount of water a river carries
- Ten longest rivers in the world
- note: there is always a dispute over these lists as to the exact measurement
- this list is derived from ** See [of rivers by length (wiki)]
- which measures total length of river systems (i.e., includes tributaries)
- 1. Nile (Africa; flows into Mediterranean Sea)
- 2. Amazon (South America; flows into Atlantic Ocean)
- 3. Yangtze (China; flows into East China Sea
- 4. Mississippi (North America; flows into Gulf of Mexico)
- 5. Yenisei (Mongolia-Russia; flows into Kara Sea, part of the Arctic Ocean)
- 6. Yellow or Huang He (China; flows into Bohai Sea, part of the Yellow Sea)
- 7. Ob (northern-central Asia; flows into the Gulf of Ob, feeding into the Kara Sea, part of the Arctic Ocean)
- 8. Rio de la Plata-Parana (South America; flows into the Rio de la Plata estuary, which flows into the Atlantic Ocean)
- 9. Congo (Central Africa; flows into the Atlantic Ocean
- 10. Amur (northern-central Asia, flows into the Sea of Okhost, part of the Pacific Ocean)
- See also [Top 10 Largest Rivers in the world]
- Click EXPAND to see list of the ten longest rivers
stream
oasis
- See Ancient Egypt outline
See also:
- Hydrology / water cycle
atmosphere
winds
- Trade winds: blow from east to west (generally)
- Westerlies: blow from west to east (generally
- these winds defined oceanic travel during the "age of sail" (wind-powered boats)
- they also defined location and direction of European expeditions during the Age of Discovery
- ex. the Portuguese discovered Brazil because their ships had to sail west, across the Atlantic in order to catch the winds and currents that would then carry their ships south and east to cross the Cape Peninsula and the Cape of Good Hope (southern tip of Africa)
- windward v. leeward
- windward = upwind, or that side facing or nearest to the incoming wind
- leeward = downwind, or that side facing away or furthest from the incoming wind
- see the Lesser Antilles for the "Leeward" and "Westward" Islands
Land forms
archipelago
- a series of geographically proximate or geologically similarly island, usually formed in a chain or a cluster
basin
butte
cape
- a "headland", "promontory" or large body of land that extends into a larger water body, usually an ocean or a sea
- "headland" is a "coastal landform," usually with a high point and cliffs
- "promontory" is a raised land body that extends into lower land or water
- promontories are often used a defensive positions for forts, castles and defensive positions
- a promontory in water is a peninsula
- Click EXPAND for a list of important capes:
- Cape Canaveral - Florida
- Cape Cod - Massachusetts
- Cape Discord - Greenland
- Cape of Good Hope - South Africa
- Cape Horn - Chile
- southernmost headland, or tip of land, on Hornos Island, one of the Hermite Islands, the southernmost of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago at the southern tip of South America
- northern boundary of the Drake Passage
- Cape Kidnappers - New Zealand
- Cape Three Forks - Morocco
- Cape Vert - Senegal; the westernmost point of Africa
canyon
- a "cleft" or opening with steep cliff walls on either side
- canyons are usually formed by erosion from rivers
- but can also be caused by "weathering" (see definition under geology entry)
- also called a gorge

- narrows or slot canyon is a very narrow canyon and can extend for some distance
- see "The Subway," a slot canyon in Zion National Park, Utah
continent
- largest continuous unit of a land form or land mass
- * except for Europe (and, thus Asia), continents have defined perimeters
- continents are defined by extent, separation, tectonic plates (some have multiple plates)
- click on EXPAND to see list of Continents
- ordered by size, largest to smallest:
- Asia
- may also include Europe, which would be "Eurasia"
- Africa
- North America
- South America
- Antarctica
- Europe
- Australia
- disputed continents
- Australia
- sometimes considered world's largest island
- Europe
- Europe is technically not a continent, but if so, neither is Asia
- considered together, Europe + Asia = "Eurasia"
- the concept of Europe as a continent is traditional and cultural, but still valid geographically
- Europe is technically not a continent, but if so, neither is Asia
- click EXPAND for more on definition of Europe as a continent
- to the ancient Greeks, Europe was the "Land of the West"
- and Asia was the "Land of the East:
- and Africa was called "Libya"
- as a continent, Europe is divided from Asia by
- Ural Mountains (in Russia)
- Bosporus Strait (at Constantinople, Turkey)
gorge
- another name for canyon (see above)
hill
island
isthmus

- land-form that has large water bodies on opposite sides
- and connects two larger land forms
- also called a "land bridge"
- plural form = "isthmuses"
- examples:
- Karelian Isthmus << connects Russia to Finland
- Kra Isthmus << connects southeast Asia to the Malay peninsula
- Panama << connects North and South Americas
- Sinai << connects northeast Africa to southwest Asia
- canals are usually built across isthmuses
- Panama Canal
- Corinth Canal
- Suez Canal
land-bridge
- a small or especially narrow isthmus
mountain
peninsula
plateau
tectonic plates
trench
- trench
- a large, narrow (as compared to length) depression in the ground or underwater
- trenches are caused by erosion, glaciers, or movement of tectonic plates
- trenches can be on land or under water, such as the Mariana trench, deepest
- smaller forms of a trench are called a "gully" or a "ditch"
- larger trenches caused by tectonic plate movements are also called "rift valleys"
- volcano
volcano
- formed when magma from below breaks through the earth's crust
- when that happens, lava, ash, and gasses escape from the earth's hot mantle
- as lava accumulates and hardens, volcanic mountains, below and above the seas form
- two principle of volcanos:
- conical volcano
- the most common type of volcano with high walls and a cone at the top
- built up by layers (or "strata") of lava and other airborne, solid "fragments" of ash and cinders
- in a conical volcano the lava flow hardens before spreading far
- stratovolcano (or composite volcano from layers of lava flows), spatter cone (from a lava fountain)
- see also cinder, rootless, and tuff cones: Volcanic cone - Wikipedia
- shield volcanos
- the lava flows outward and the volcano does not build up like a conical volcano
- conical volcano
- there are various types of volcanic eruptions
- the earth's crust itself is originally built of lava
- = "igneous rock"
- "igeneous" is from ignis, Latin for "fire"
- other rock types:
- sedimentary = layered minerals and organic material
- metamorphic = new rock types formed by pressure and heat of existing rocks
- = "igneous rock"
- breaks in the earth's crust are caused by
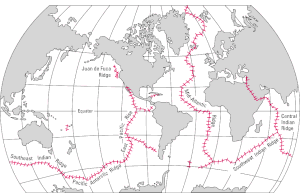
World distribution of mid-oceanic ridges - shifts in and colliding of tectonic plates
- thus places where the plates are either separating for converging, such as:
- separating = mid-oceanic ridges, which surround several of the continents, including:
- Mid-Atlantic ridge from Greenland to southern Atlantic, in the center of the Atlantic Ocean
- Pacific ridges, which extend from Baha California south and east, below Australia and connecting with the mid-Oceanic ridges of the Indian Ocean
- converging (crashing into one another), such as:
- the "Ring of Fire"
- separating = mid-oceanic ridges, which surround several of the continents, including:
- weakening or thinning of the crust, such as:
- East African Rift
- Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field in British Columbia, Canada
- Rio Grande Rift: from below the Colorado Plateau to the northern border of Mexico, covering most of New Mexico and parts of Arizona
- note: the eastern edge of the Rio Grande Rift forms the North-South vertical portion of the New Mexico-Texas natural border
- Sources:
- [Landform (National Geographic)]
Major world regions

- major regions
- there are many regions and sub-regions and different sources will define these regions differently
- world geography is broadly divided or categorized into:
- 6 or 7 continents
- 12 regions
Geoscheme regions
- classification of regions per continent
- the United Nations uses "geoscheme" system to define major world regions
- See [List of Physiographic Regions per continent (wiki)]
- below are listed the geoscheme regions per continent:
Americas
- North America
- Central America
- South America
- Caribbean
Asia
- Central Asia (Russian Asia, Mongolia)
- East Asia (China, Korea, Japan)
- South Asia (Indian sub-continent)
- Southeast Asia (Vietnam, Thailand, Malyasia, Indonesia, etc.)
- West Asia (Middle East)
- Asia Minor, Anatolia
Africa
- East or Eastern Africa
- Horn of Africa = the peninsula of east Africa between the Red Sea and the Indian Ocean
- = the easternmost point of Africa
- Horn of Africa = the peninsula of east Africa between the Red Sea and the Indian Ocean
- North or Northern Africa
- South or Southern Africa (not the nation "South Africa")
- Sub-Saharan Africa
- West or Western Africa
Australia
Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Scandinavia
- Europe is also classified according to
- ethnicity
- language
- religion
Other major regions terminology
- Eurasia
- Mediterranean
- Latin America
World oceanic regions
- Mediterranean
- Arabian Sea
- Indian Ocean
- Atlantic Ocean
- Pacific Ocean
- Gulf of Mexico
- Caribbean Sea
- China Sea
- North Sea
- Macaronesia (Atlantic)
Oceania

- Oceania
- Pacific region in general, divided into
- Australasia
- Melanesia
- Micronesia
- Polynesia
- List of independent nations of Oceania:
- Australia
- East Timor
- Federated States of Micronesia
- Fiji
- Indonesia
- Only Papua, or Indonesian New Guinea is part of Oceania, whereas the rest of Indonesia is located in Southeast Asia
- Kiribati
- Marshall Islands
- Nauru
- New Zealand
- Palau
- Papua New Guinea
- Samoa
- Solomon Islands
- Tonga
- Tuvalu
- Vanuatu
- Also:
- Cook Islands and Niue are "associated states" with New Zealand
- Click EXPAND to see list of independent nations of Oceana
- See [List of sovereign states and dependent territories in Oceania (wiki)]
Macaronesia
- island region in Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Portugal and West Africa
- volcanic islands
- Macaronesia consists of:
- Azores islands
- Portuguese territories
- Canary Islands
- Portuguese territories
- Madeira islands
- Spanish territories
- Cape Verde
- officially "Republic of Cabo Verde"
- it won independence from Portugal in 1975
- a democratic republic
- named for Cape Vert in Senegal, which is directly east of Cape Verde
- consists of 10 volcanic islands
- officially "Republic of Cabo Verde"
Climate
Climate Zones
see also : [Climate (Geography)]
- Roaring Forties
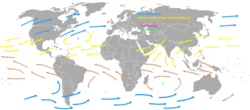

- westerly winds that cross from west to east along the southern hemisphere 40-50th parallels
- the Roaring Forties aided age of sail shipping routes from south of Africa to Australia
- and from Australia/New Zealand to the southern tip of South America
Geology & geological processes
Land forms processes
- erosion = the transport or movement of rocks and soil by water or wind
- erosion spreads silt (important for farming), forms canyons, coastlines, and other surface features
- types or causes of erosion:
- rivers
- rain/snow fall
- tides/waves
- atmospheric (wind, gasses)
- glaciers
- see [Erosion (wiki)]
- weathering = breakdown of rocks and soil from contact with water, the atmosphere, and organisms
- weathering is not erosion, as weathering does not include transit of rocks and soil
Hydrology cycle
Water forms processes
- waves = oscillations
- waves in water are technically "wind waves"
- water waves are caused by winds
- underwater waves
- ocean floor topography causes underwater waves
- highest underwater waves occur in the Luzon Strait between Taiwan and the Philippines
- caused by two parallel underwater ridges
- some underwater waves there can be as high as 1,600 feet
- see " Geoffrey Giller, “Long a Mystery, How 500-Meter-High Undersea Waves Form Is Revealed.” ©2014 by Scientific American
Human populations
Language groups
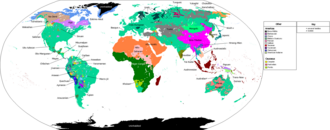
- there are 15 major language families in the world
- each of these major groups have sub-groups of distinct languages
- there are 7,111 languages in the world
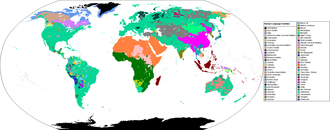
- there are also many other distinct languages (see map)
- see List of language families (wikipedia)